The plant life cycle is a fascinating journey that begins with a seed and ends with the creation of new seeds. Understanding this cycle helps us appreciate the essential role plants play in our ecosystem and their various stages of growth and development.
[Scroll Down for Download Link]
Learn the Plant Life Cycle

Let’s learn about plants. All living things, plants, have a lifecycle.
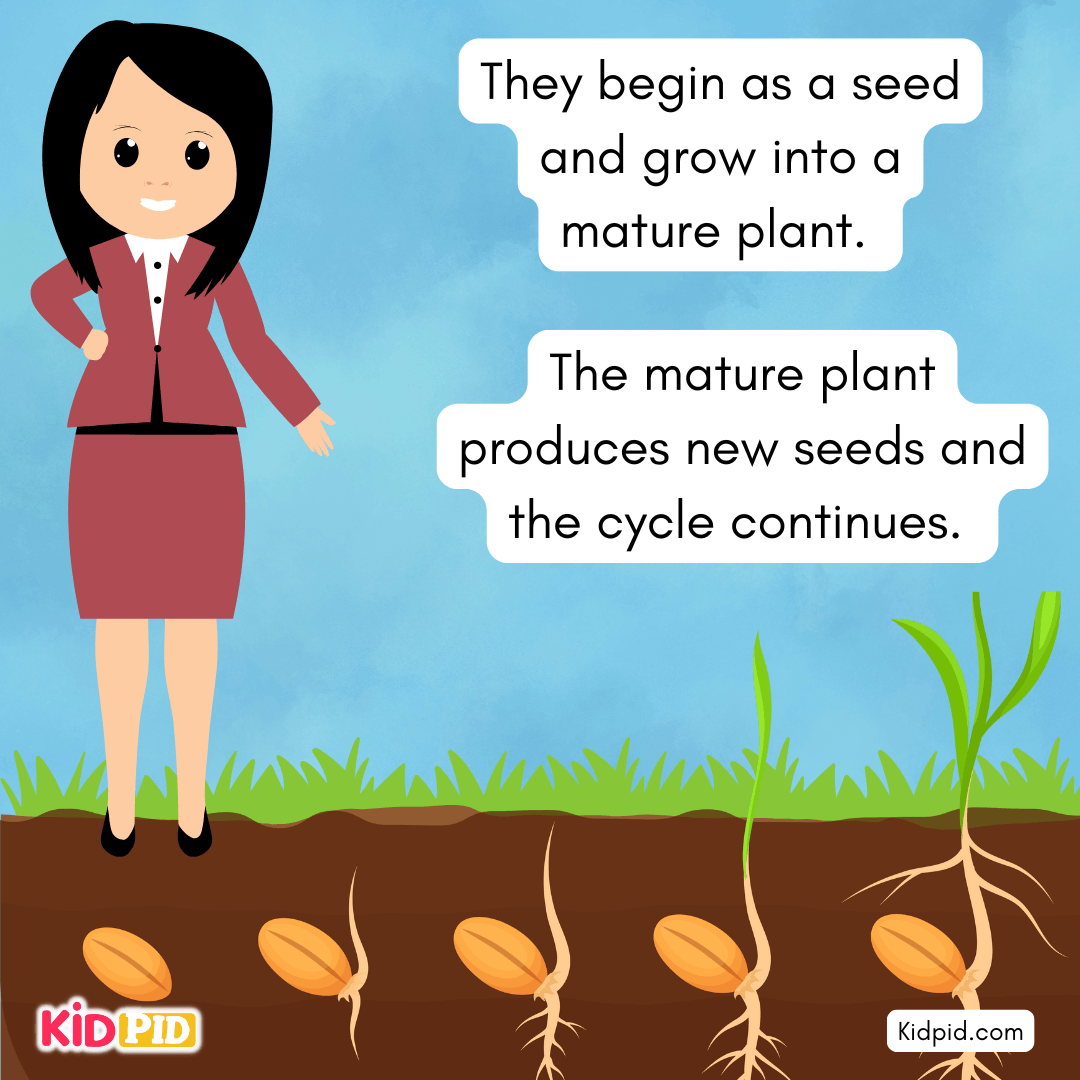
They begin as a seed and grow into a mature plant. The mature plant produces new seeds, and the cycle continues.
However, not every plant produces seeds. Some lower plants, such as ferns and mosses, produce different types of cells called spores.

These plants also have a life cycle, but do not produce seeds.
Let’s study the life cycle stages of flowering plants.
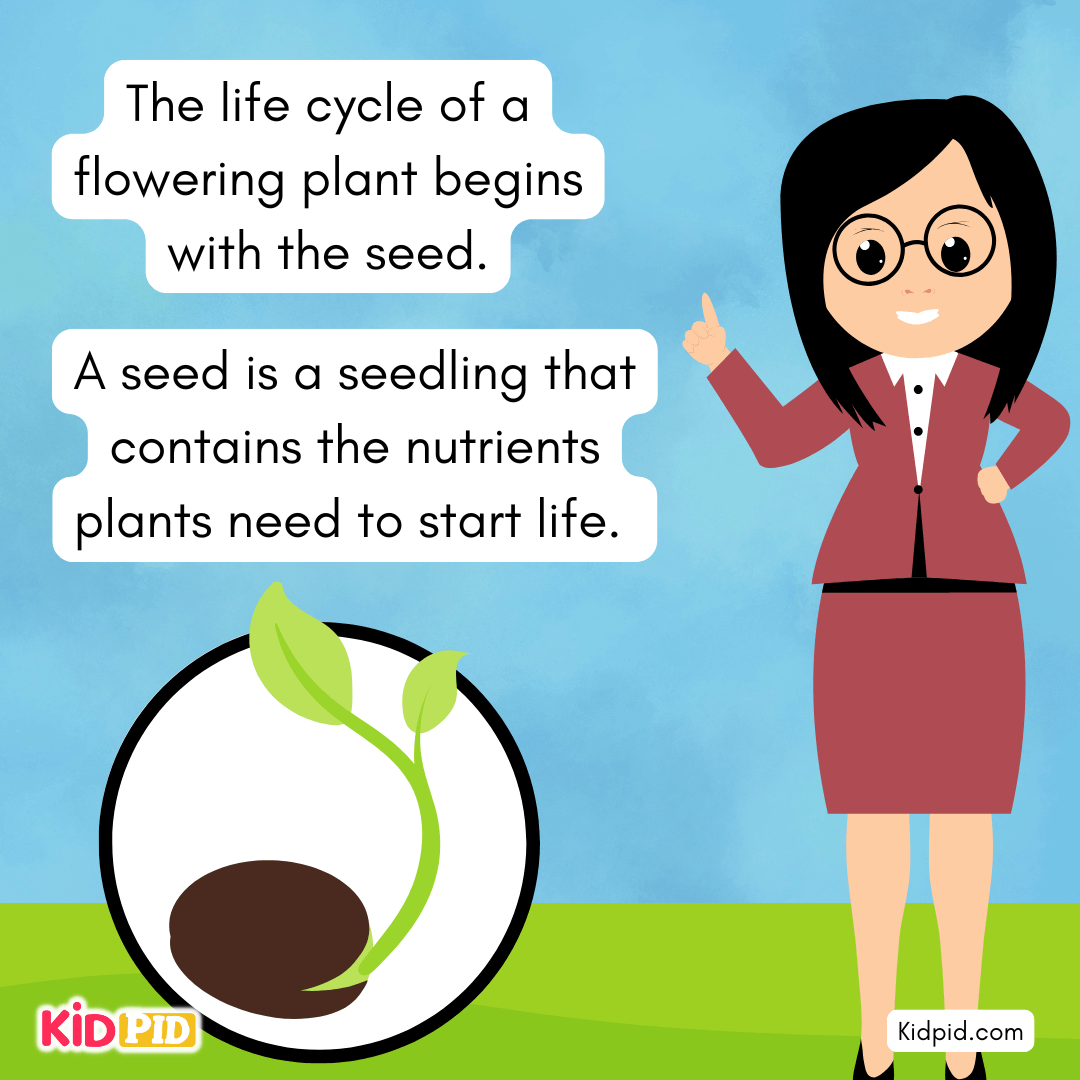
The life cycle of a flowering plant begins with the seed. A seed is a seedling that contains the nutrients plants need to start life.

Seeds can survive for years, even in winter.
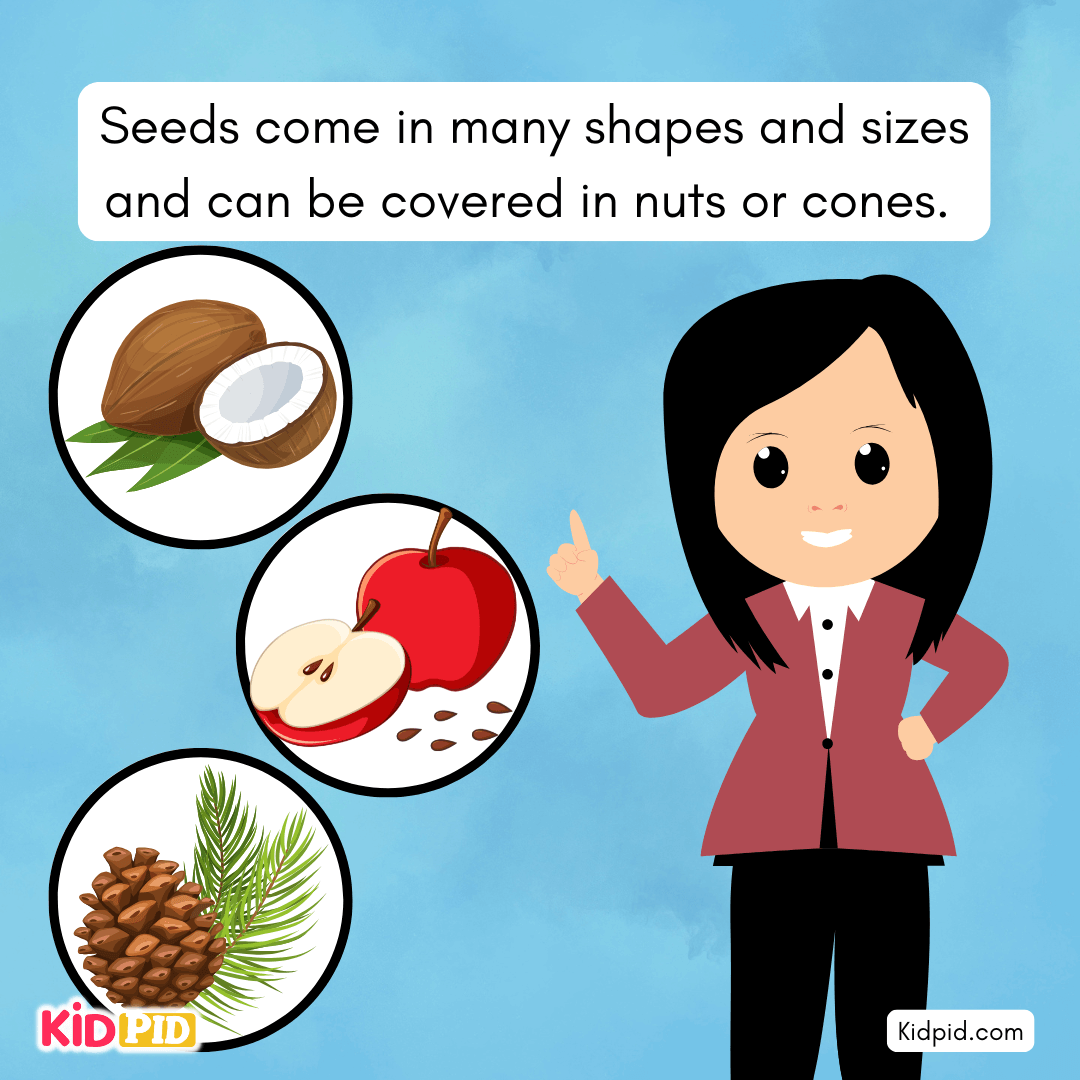

Seeds come in many shapes and sizes and can be covered in nuts or cones.

The next stage is Germination. Germination is a stage where the plant begins to grow from a seed.

The seeds will sprout when they receive light, water, and minerals. A seed will not germinate without all these.
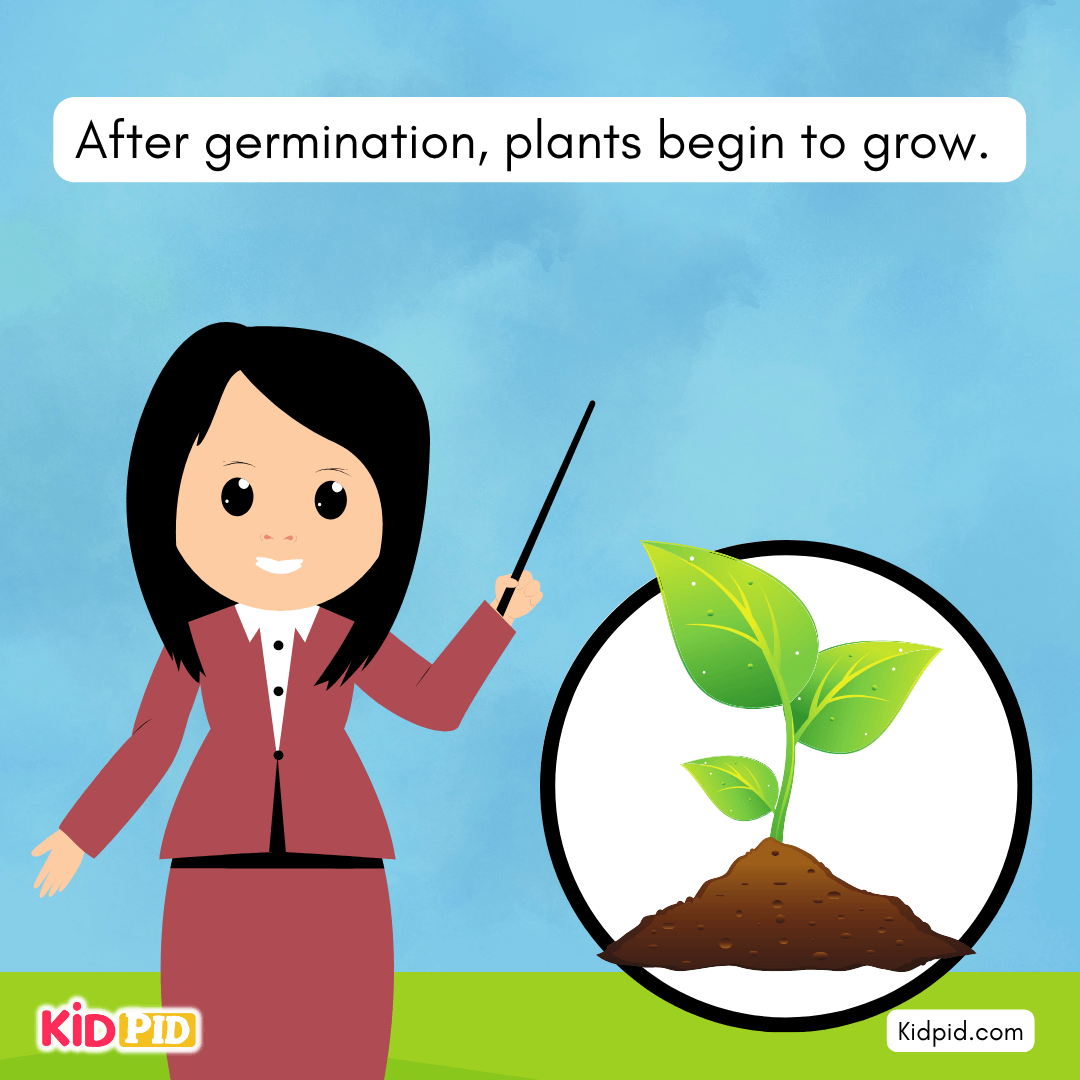

After germination, plants begin to grow.

Plants need sunlight, nutrients, water, and air to survive and grow.
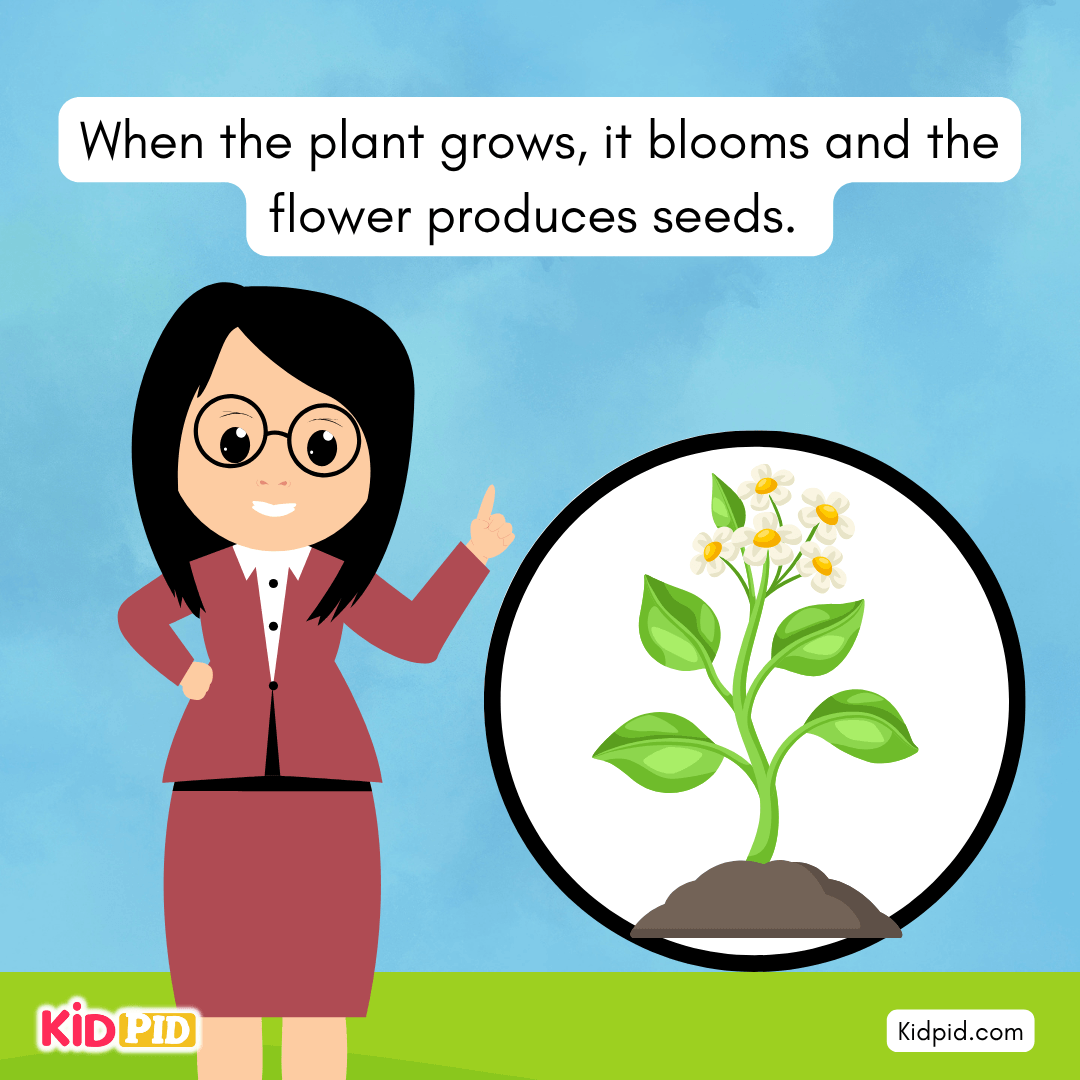
When the plant grows, it blooms, and the flower produces seeds.
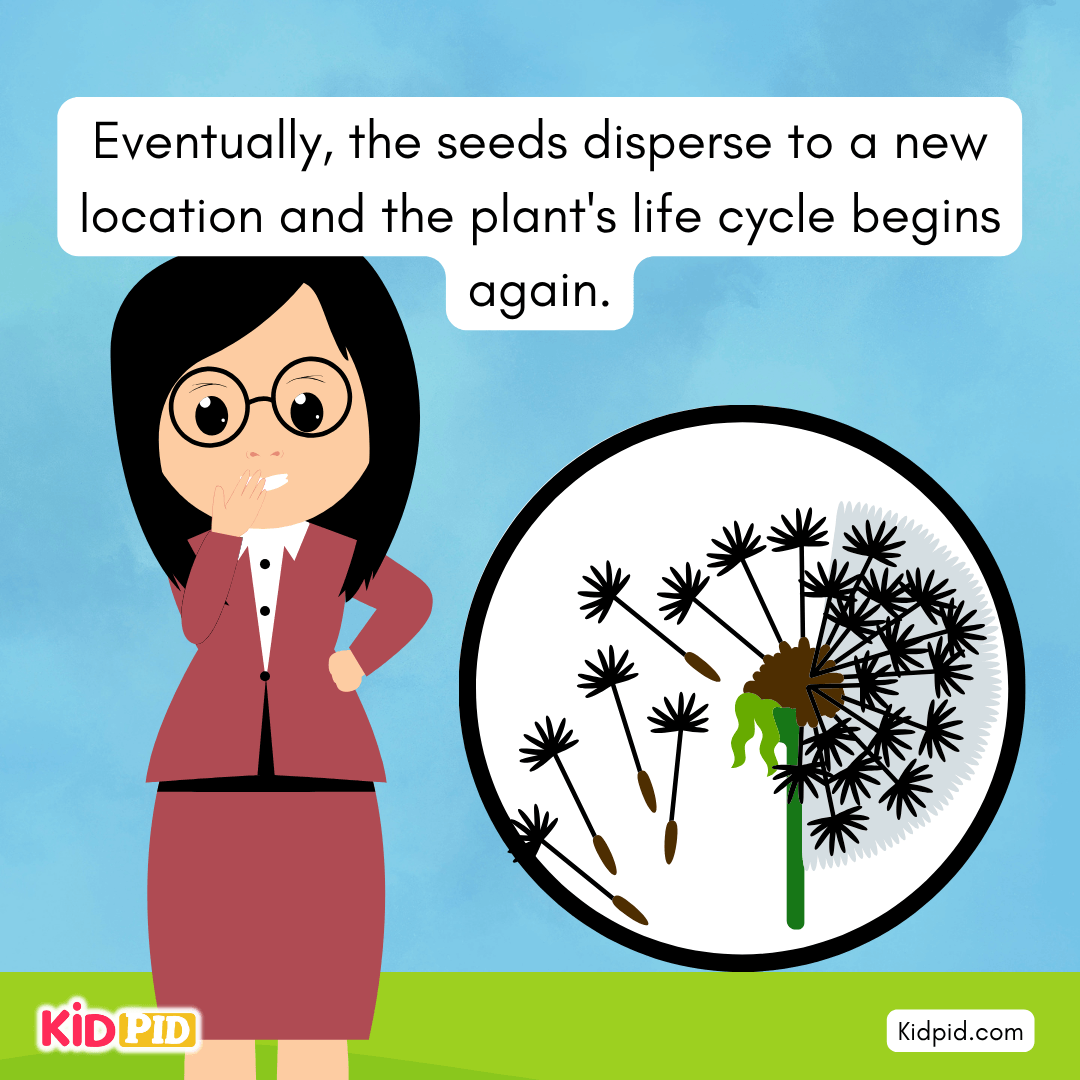
Eventually, the seeds disperse to a new location and the plant’s life cycle begins again.

Seeds can be dispersed by Wind, Water, Animals, and Explosion.
Now let’s learn more about plants and their functions.
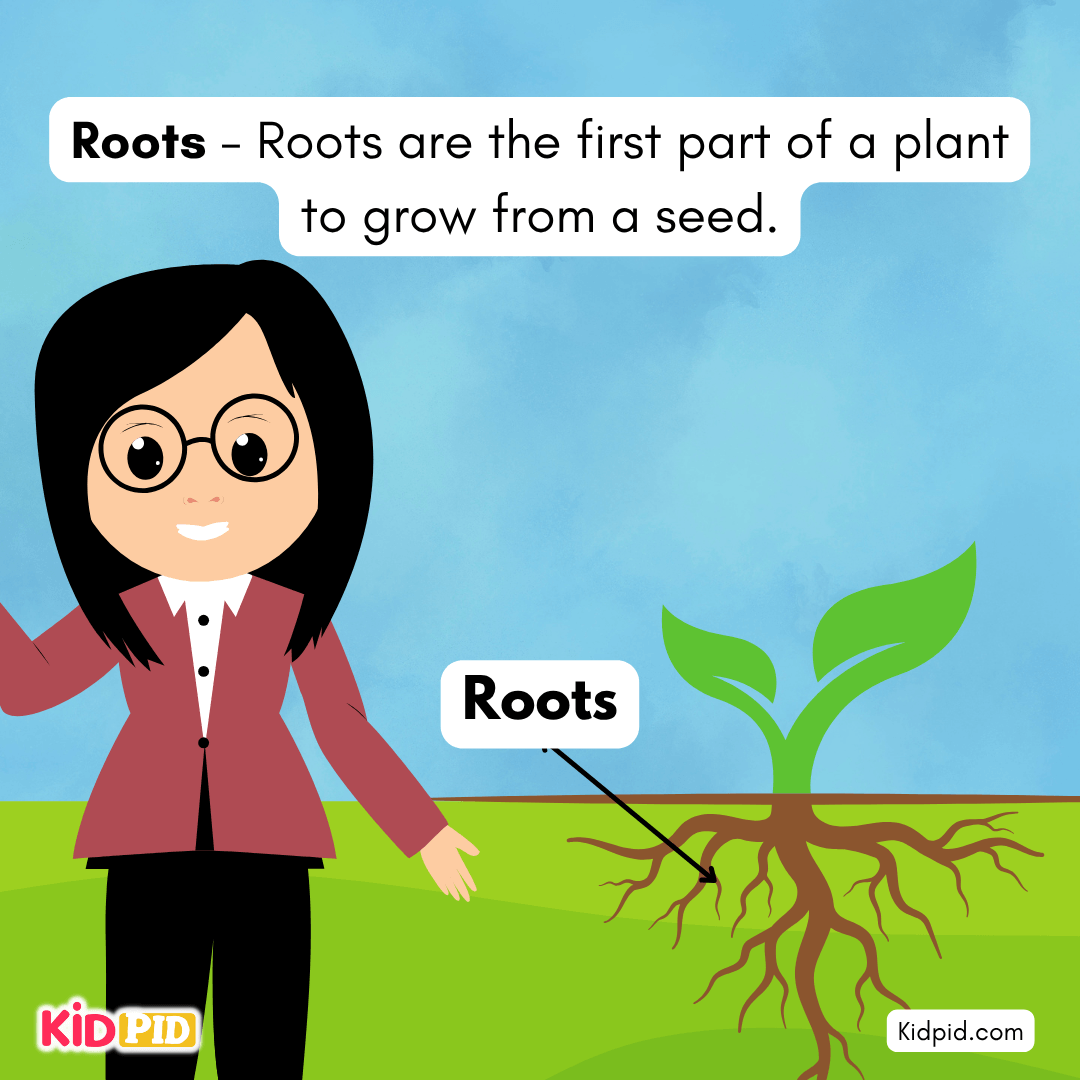
Roots – Roots are the first part of a plant to grow from a seed.
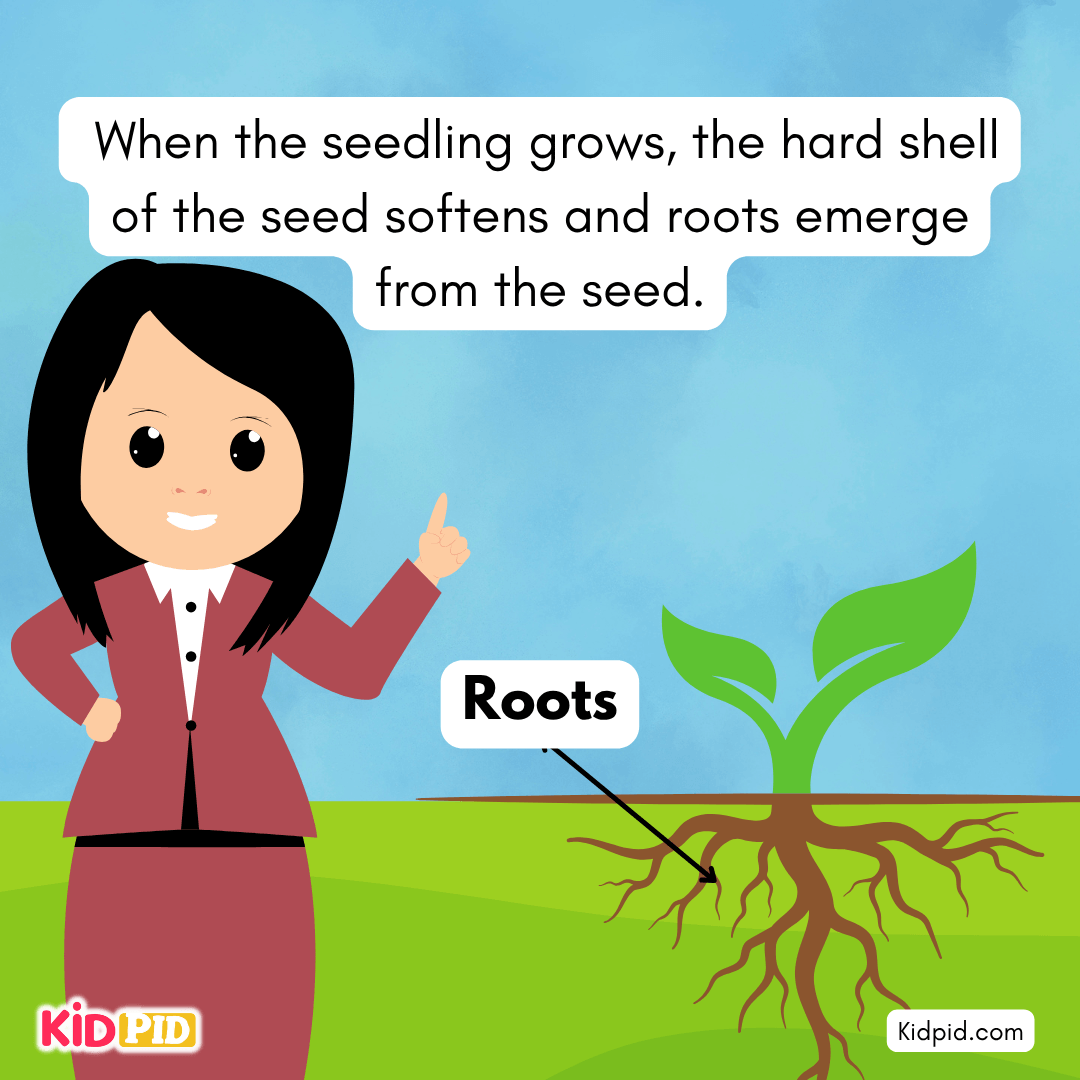
When the seedling grows, the hard shell of the seed softens, and roots emerge from the seed.

It absorbs water and minerals from the soil for plant use.
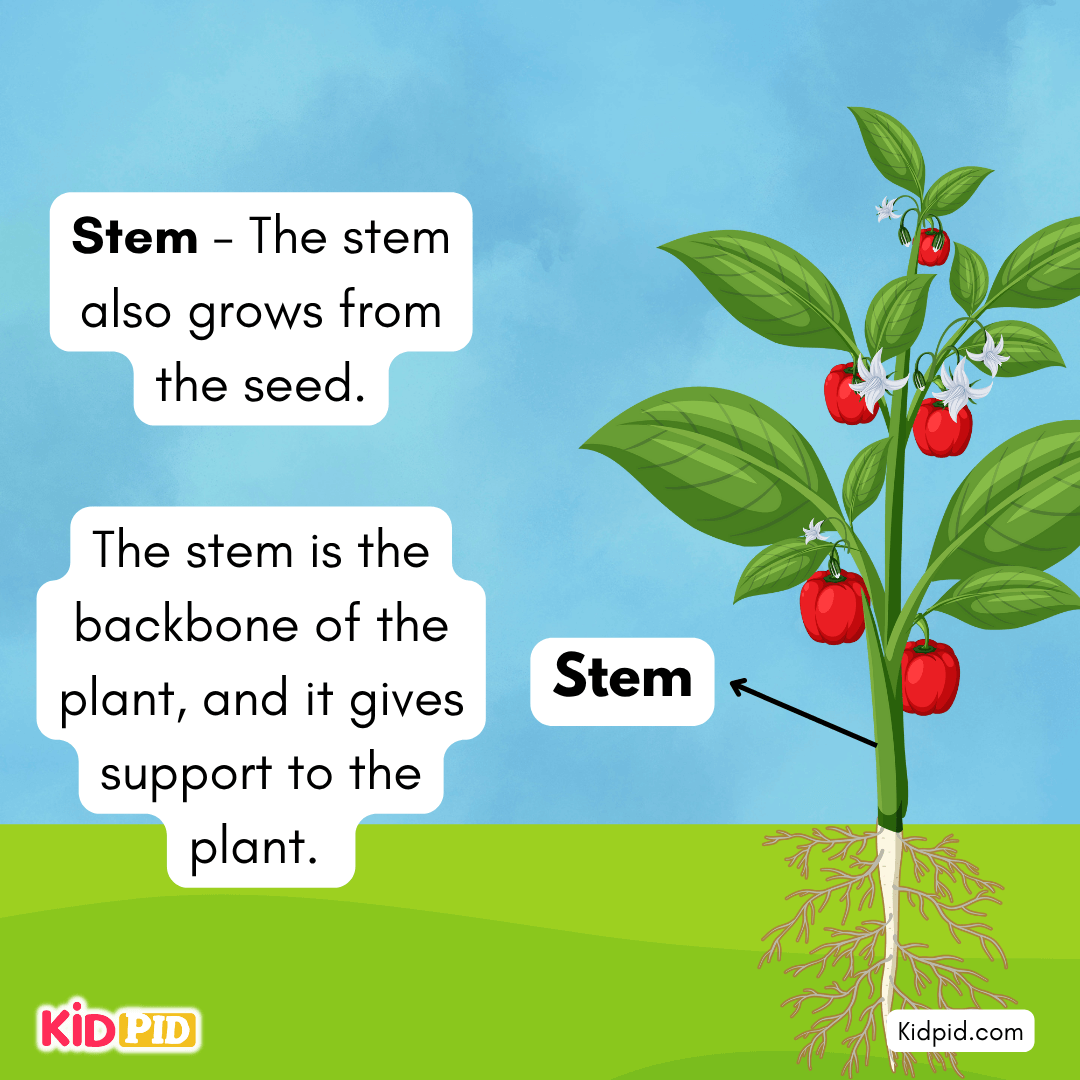
Stem – The stem also grows from the seed.
The stem is the backbone of the plant, and it gives support to the plant.
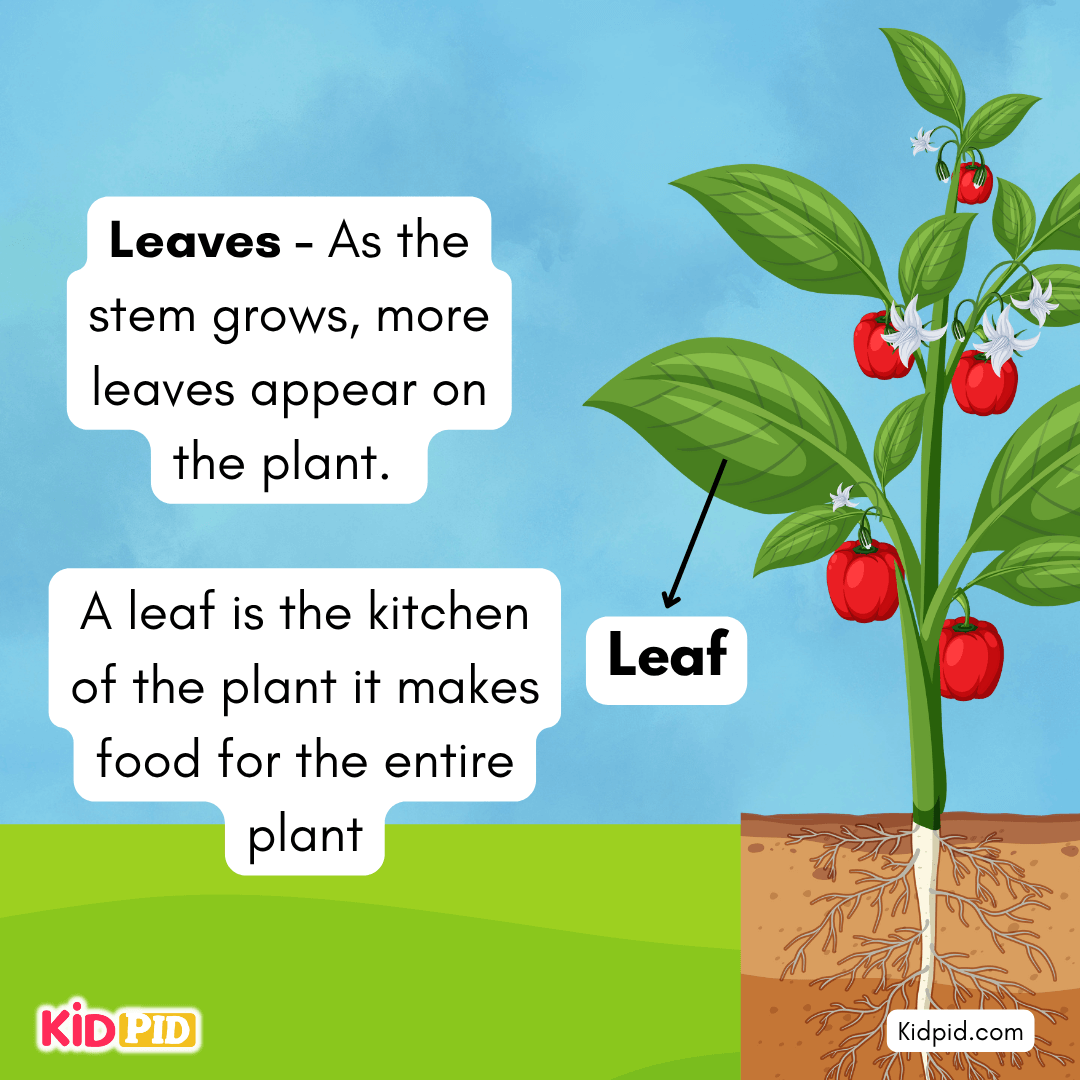
Leaves – As the stem grows, more leaves appear on the plant.
A leaf is the kitchen of the plant; it makes food for the entire plant.
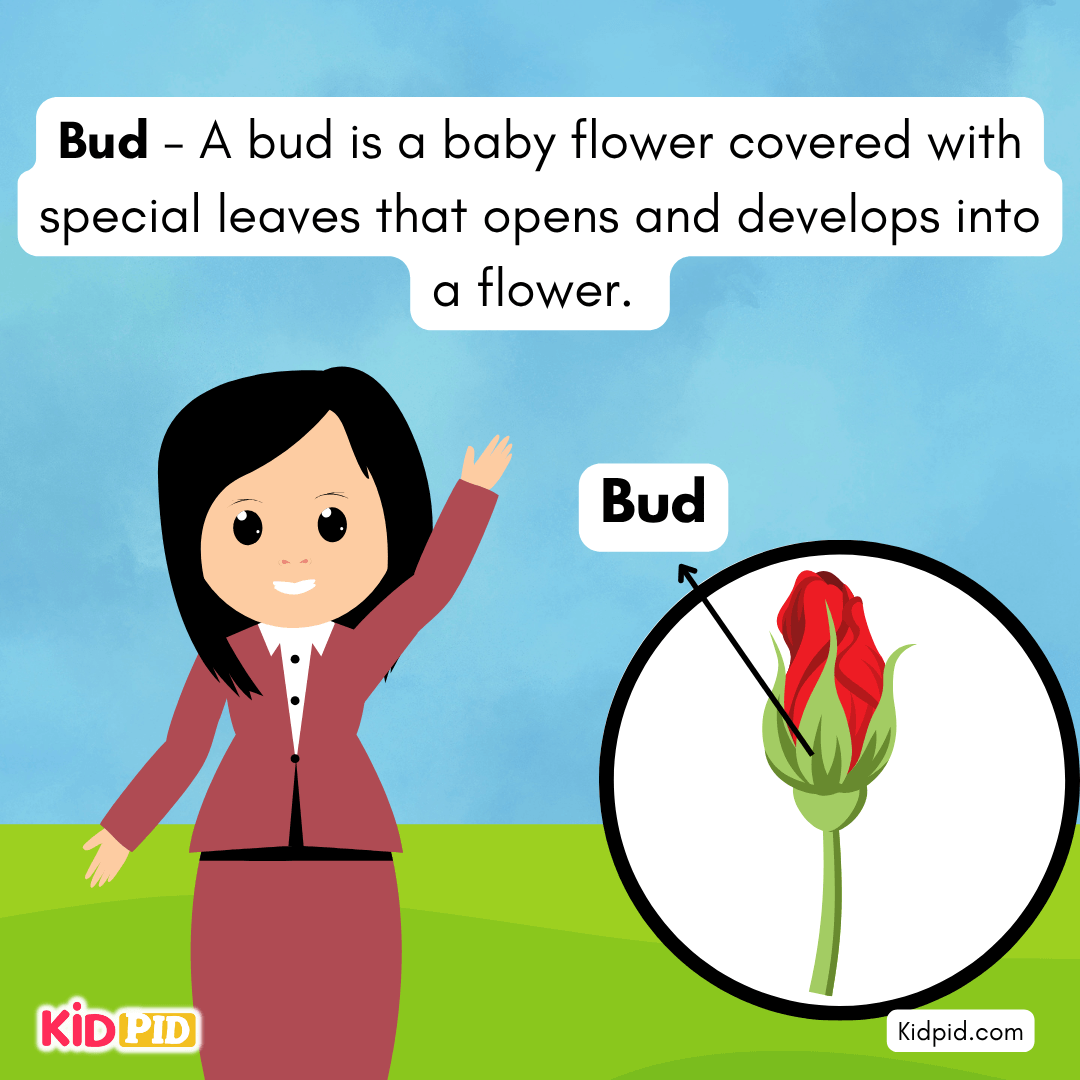
Bud – A bud is a baby flower covered with special leaves that opens and develops into a flower.
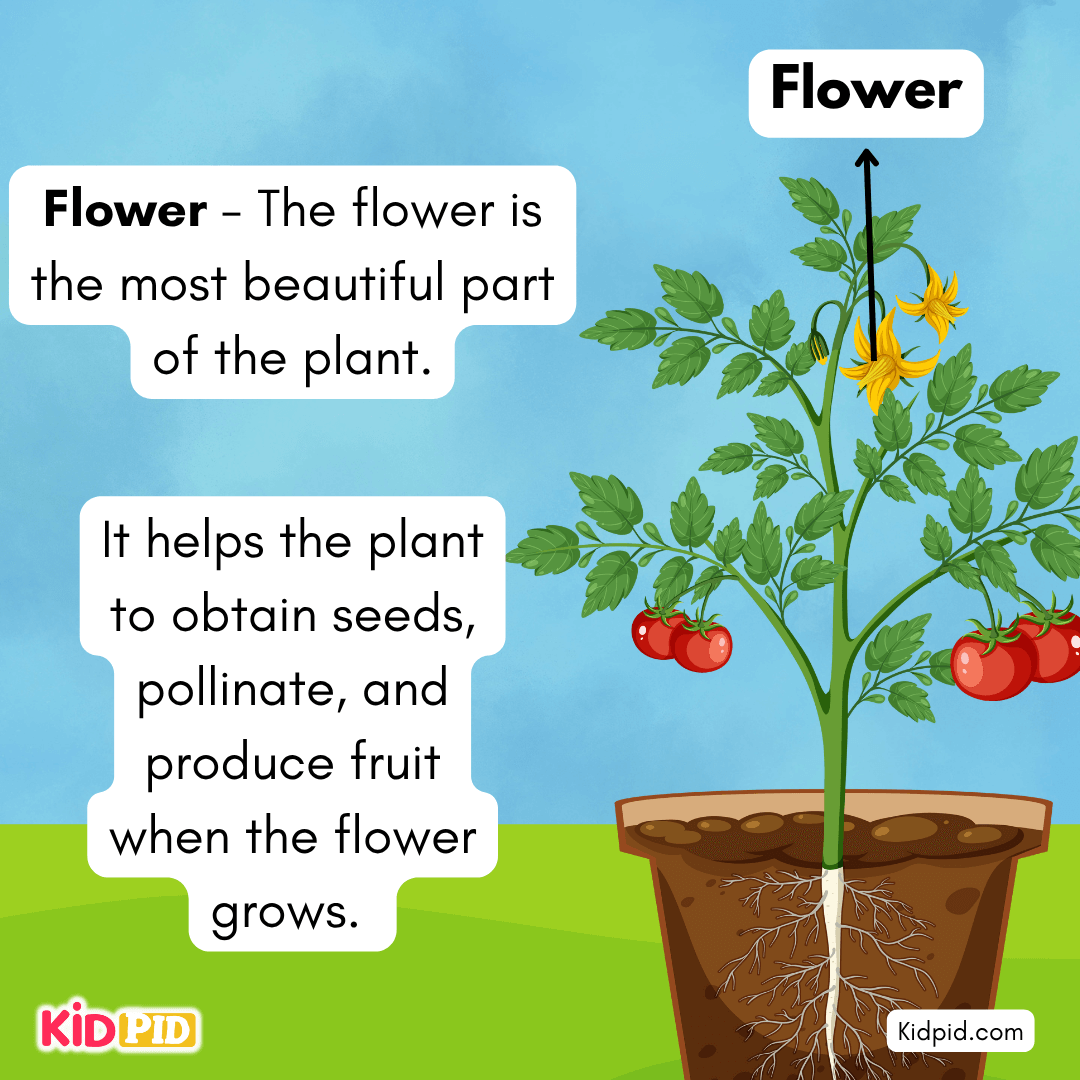
Flower – The flower is the most beautiful part of the plant.
It helps the plant to obtain seeds, pollinate, and produce fruit when the flower grows.
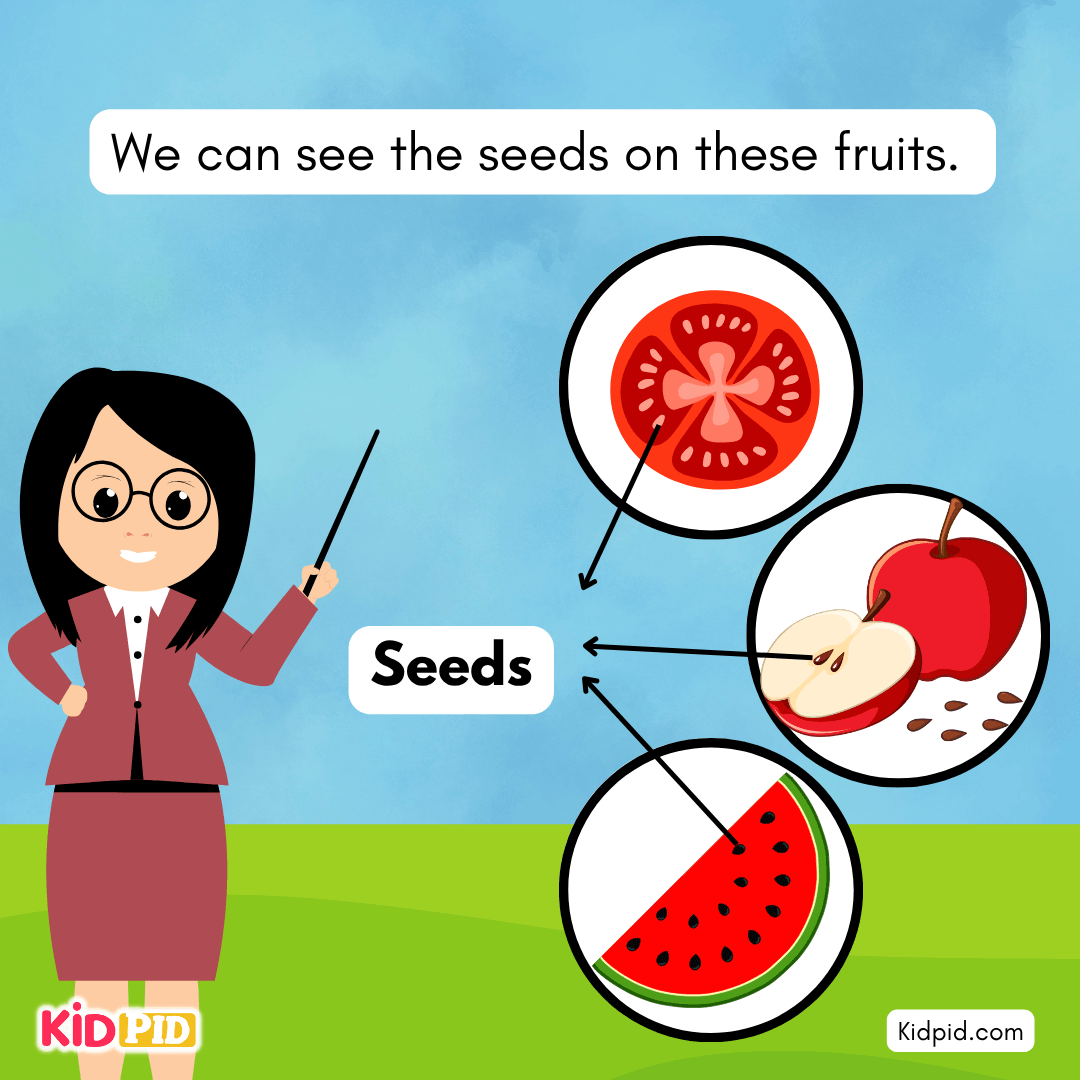
We can see the seeds on these fruits.

Let’s learn how to grow a plant

We put the seeds of the plants we want to grow into the soil.
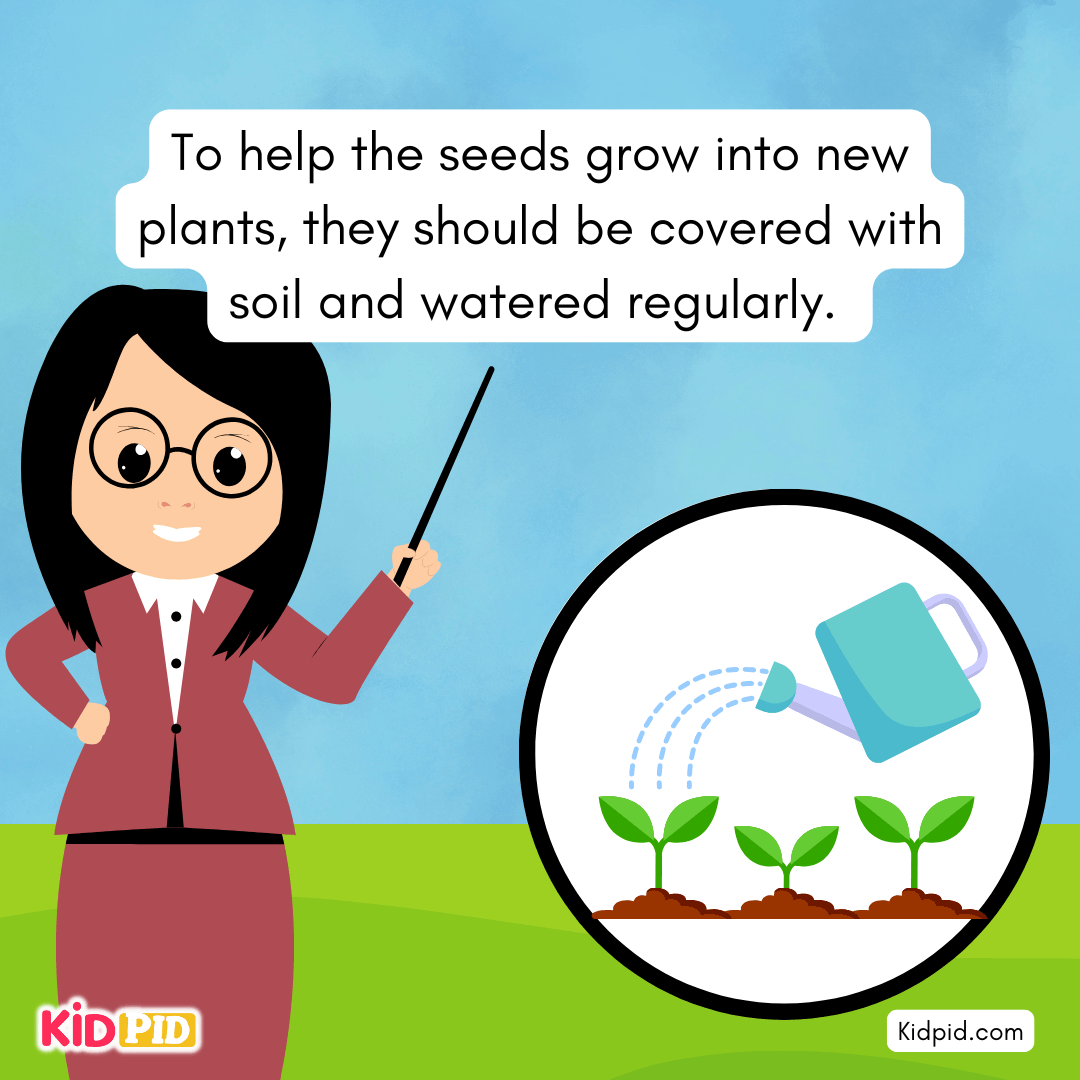
To help the seeds grow into new plants, they should be covered with soil and watered regularly.

Soon, roots and stems will grow from the seeds, and we can see the seeds emerging from the soil.
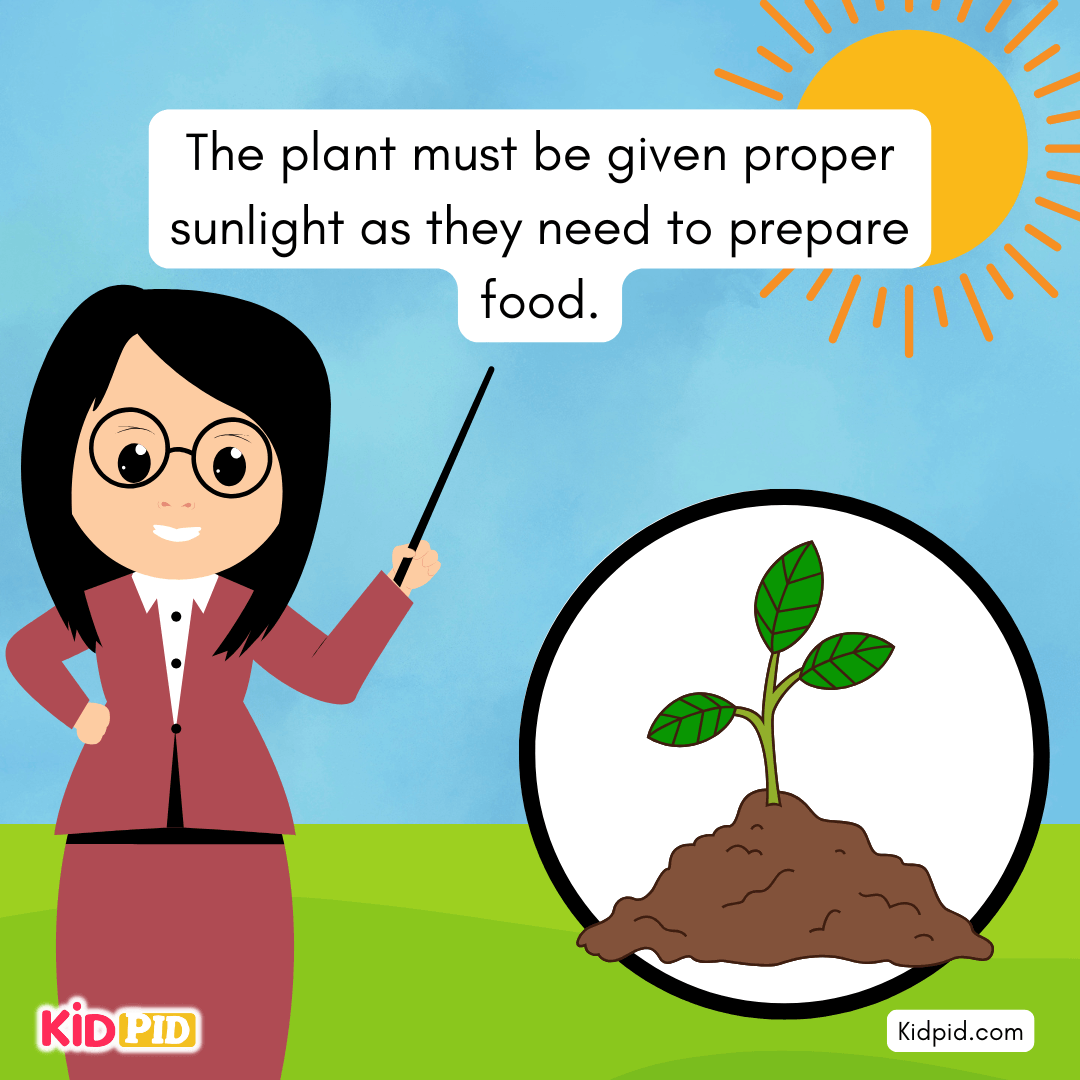
The plant must be given proper sunlight as it needs to prepare food.

In conclusion, the plant life cycle illustrates the interconnectedness of nature. From germination to seed dispersal, each stage is vital for sustaining life. By nurturing plants, we contribute to a healthier environment and ensure the continuation of this beautiful cycle. Follow us on Facebook, Pinterest, YouTube & Telegram, and join our Telegram group to access more free printables.
You may like this
Plant Life Cycle Worksheet for Kindergarten

The Plant Life Cycle Worksheet for Kindergarten helps young learners understand plant growth stages, from seed to vegetable, through engaging activities like numbering and drawing, enhancing both knowledge and vocabulary.
Paragraph on ‘The Life Cycle of a Plant’

The page provides detailed paragraphs on the plant life cycle, outlining stages from seed to adult plant. It emphasizes growth, reproduction, and the importance of plants in nature.
Paragraph on ‘The Wonders of Carnivorous Plants’

The page explores the fascinating world of plants, detailing how they capture and digest insects for nutrients, showcasing their unique adaptations to thrive in nutrient-poor environments.
Paragraph on ‘How Do Plants Grow?’

The page explains how plants grow from seeds, detailing the essential processes of photosynthesis, the roles of roots, stems, and leaves, and the importance of water, sunlight, and soil.
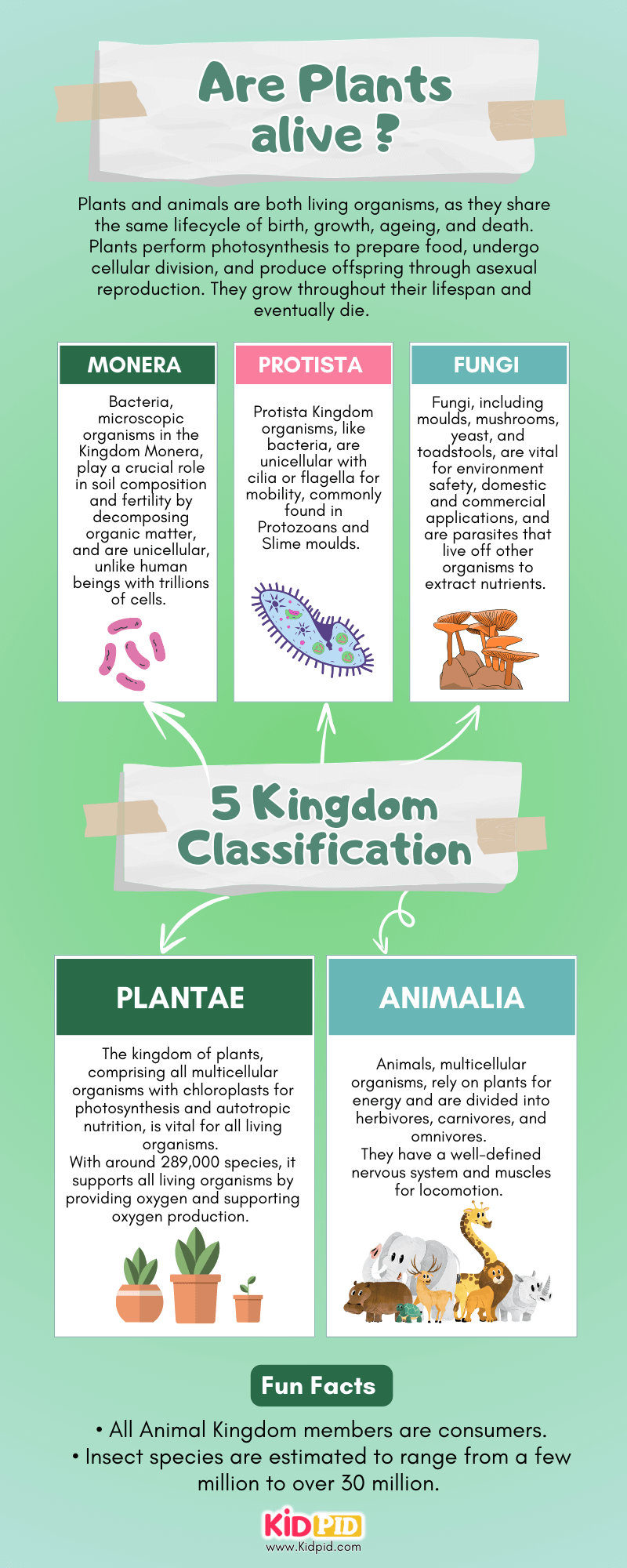
Are plants alive?
The page discusses whether plants are alive, explaining that they are living organisms that grow, reproduce, and undergo life cycles, highlighting their ability to perform photosynthesis and adapt to environments.