Hibernation is a survival strategy used by some animals to endure the cold winter months. During hibernation, animals slow down their body functions, like breathing and heartbeat, to conserve energy. This deep sleep-like state helps them survive when food is scarce and temperatures are low, ensuring their safety until spring returns.
[Scroll Down for Download Link]
Understanding Hibernation in Animals
Read More: Paragraph on ‘Hibernation and Animal Sleep’
Oh, you must be wondering why these bats aren’t waking up.

They are not sleeping; they are hibernating. Let’s learn about hibernation today.

The word “hibernation” comes from the Latin word “hibernare,” which means to spend the winter in deep sleep.

During this time, it may be difficult for animals to find enough food.
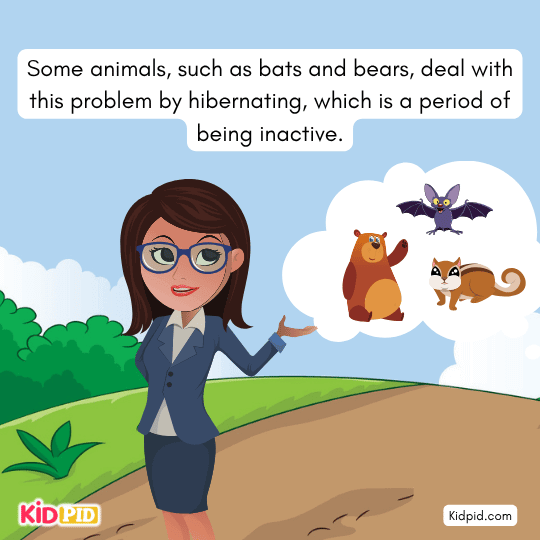

Some animals, such as bats and bears, deal with this problem by hibernating, which is a period of being inactive.

Hibernation is a type of deep sleep that helps animals conserve energy and survive the cold winter season without much food.

When an animal hibernates, its body temperature and breathing rate decrease, so it does not consume much energy.

In warm weather, bears come out of hibernation and return to their usual activities.

During hibernation, bears can use their urine and proteins again, so they don’t have to go to the bathroom all winter.
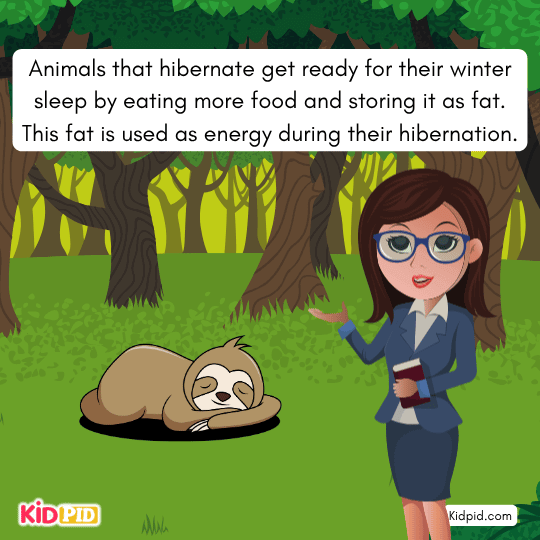

Animals that hibernate get ready for their winter sleep by eating more food and storing it as fat. This fat is used as energy during their hibernation.
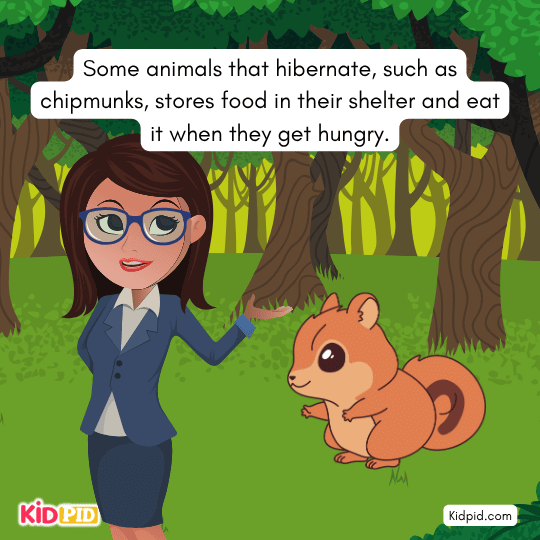

Some animals that hibernate, such as chipmunks, store food in their shelter and eat it when they get hungry.

Some animals that hibernate, such as fish, frogs, and turtles, hide under stones, logs, dirt, and leaves in the water, and come out when the weather is nice.

Paper wasps, yellowjackets, and some mosquitoes look for a safe place to stay when it’s cold outside, until the weather gets warmer again.
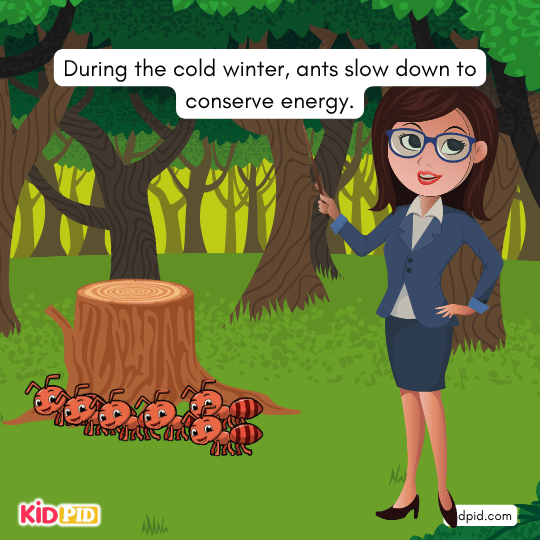

During the cold winter, ants slow down to conserve energy.

They seek out warm places like underneath rocks or tree bark, gather around the Queen, and eat the fats, proteins, and carbs they have saved up from the fall.

Let’s look at some birds that hibernate. Many ornithologist say that the Common Poorwill is believed to be the only bird species that hibernates

Bears, not all species of bear hibernate, female may have their babies during hibernation.

Bats, on average, can hibernate for up to 64 to 66 days.

Fat-tailed dwarf lemurs are the only type of primate that is known to hibernate.
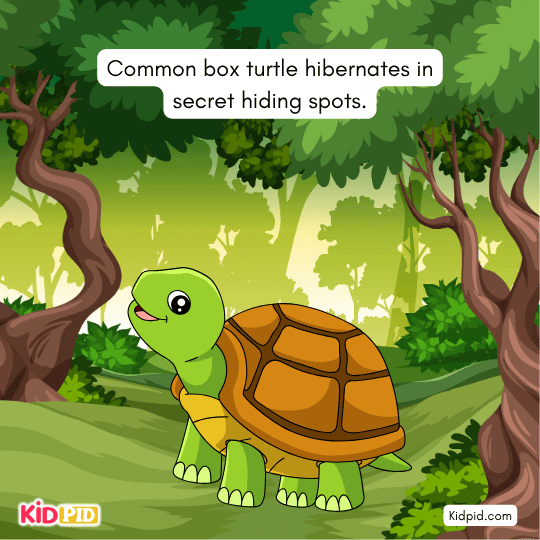

The common box turtle hibernates in secret hiding spots.

Bumblebees, males, and worker bees die, while the queen survives by hibernating through the winter.
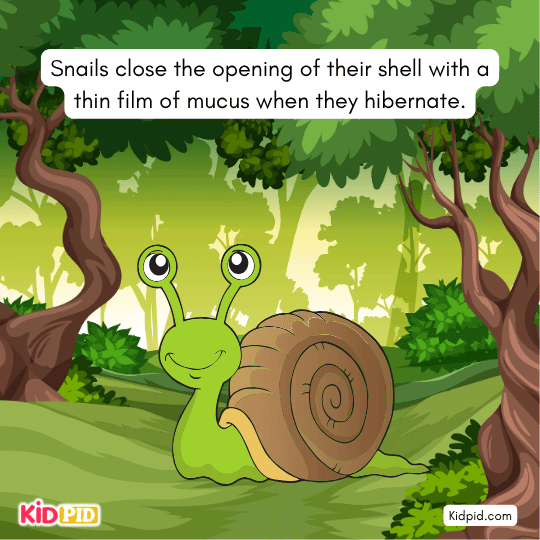

Snails close the opening of their shell with a thin film of mucus when they hibernate.

And Hedgehogs, some of them do not go into hibernation, while others hibernate for long periods.
Hibernation helps animals survive harsh winter conditions by conserving energy when food is scarce. During this period, their body functions slow down significantly. This natural adaptation is vital for survival and reproduction in many species, ensuring they emerge healthy and ready for spring when resources become available again.
You may like this:
Why do some animals hibernate?

Discover why animals hibernate during winter with simple explanations, helping kids understand animal behavior and seasonal changes in nature.
How does hibernation work?

Learn how hibernation works in animals with simple facts, helping kids understand body changes and survival during winter sleep.
How do caterpillars turn into butterflies?
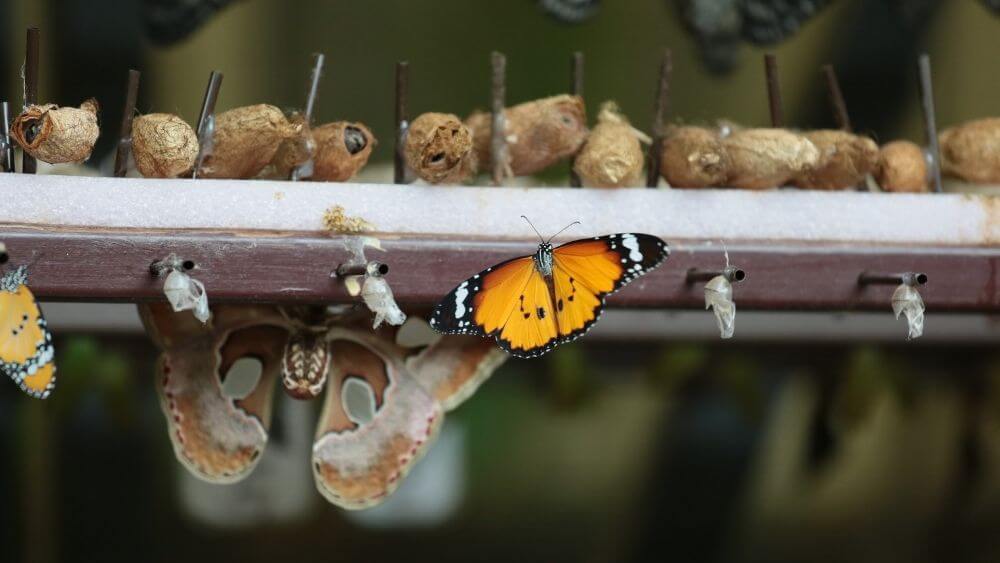

This article explains how caterpillars turn into butterflies through metamorphosis, teaching kids about insect life cycles in a simple way.
How do plants and animals adapt to their environments?

This article teaches kids how plants and animals adapt to their environments for survival using simple language and colorful examples.
Paragraph on ‘Why We Should Protect Polar Bears’

This article explains why we should protect polar bears, highlighting their importance in nature and the effects of climate change.