Have you ever wondered how planets move in space? A long time ago, a scientist named Johannes Kepler discovered important rules that explain how planets travel around the Sun. These rules help us understand the paths, or orbits, that planets take. Let’s explore Kepler’s laws and how they describe planetary motion!
- Who Was Johannes Kepler: Kepler was a scientist who studied the movement of planets in the early 1600s.
- What Are Kepler’s Laws: Kepler’s laws are three important rules that explain how planets move around the Sun.
- First Law: Elliptical Orbits: Planets move in oval-shaped paths called ellipses, not perfect circles.
- Second Law: Speed of Planets: A planet moves faster when it is closer to the Sun and slower when it is farther away.
- Third Law: Distance and Time: The farther a planet is from the Sun, the longer it takes to complete one orbit.
- Why Are Kepler’s Laws Important: These laws help scientists understand how our solar system works and predict where planets will be in the future.
- Exploring Space: Learning about Kepler’s laws lets us appreciate the amazing dance of planets in our universe!
Kepler’s Laws Describe How Planets Move And Their Orbital Paths.
Related MCQ’S
1. What is the shape of the path planets follow around the Sun?
A) Circle
B) Square
C) Ellipse
D) Triangle
2. What are the two points in an elliptical orbit called?
A) Planets
B) Foci
C) Stars
D) Axes
3. What does Kepler’s second law state?
A) Planets move in circles around the Sun
B) The radius vector sweeps equal areas in equal intervals of time
C) The planets’ paths are random
D) The Sun moves in the center of the planets
4. What does the term “radius vector” refer to?
A) The distance between two planets
B) A line joining the Sun and a planet
C) The orbit of a planet
D) The distance between the Sun and the Earth
5. According to Kepler’s third law, what does the square of a planet’s time period depend on?
A) The planet’s size
B) The planet’s speed
C) The cube of its semi-major axis
D) The number of moons it has
6. What happens as a planet’s distance from the Sun increases?
A) The planet takes less time to orbit
B) The planet’s speed increases
C) The time taken to complete a revolution increases
D) The planet moves in a straight line
7. What did Johannes Kepler publish in 1609?
A) His autobiography
B) The book Astronomia Nova
C) A book about his personal life
D) A study on solar energy
8. What is the semi-major axis of an orbit?
A) The distance from the planet to the Sun
B) Half of the minor axis of the orbit
C) Half of the major axis of the orbit
D) The longest distance between two planets
9. How long did it take Kepler to publish his next book after Astronomia Nova?
A) A few months
B) One year
C) Almost a decade
D) Two decades
10. What was one of the challenges Kepler faced in his early life?
A) He was born with weak vision
B) He had no interest in astronomy
C) He had a perfect health
D) He was not able to attend school
You may like these:
What is a planet?
A planet is a large celestial body that orbits a star, is spherical in shape, and has cleared its orbital path of debris.
Solar system and planets for kids
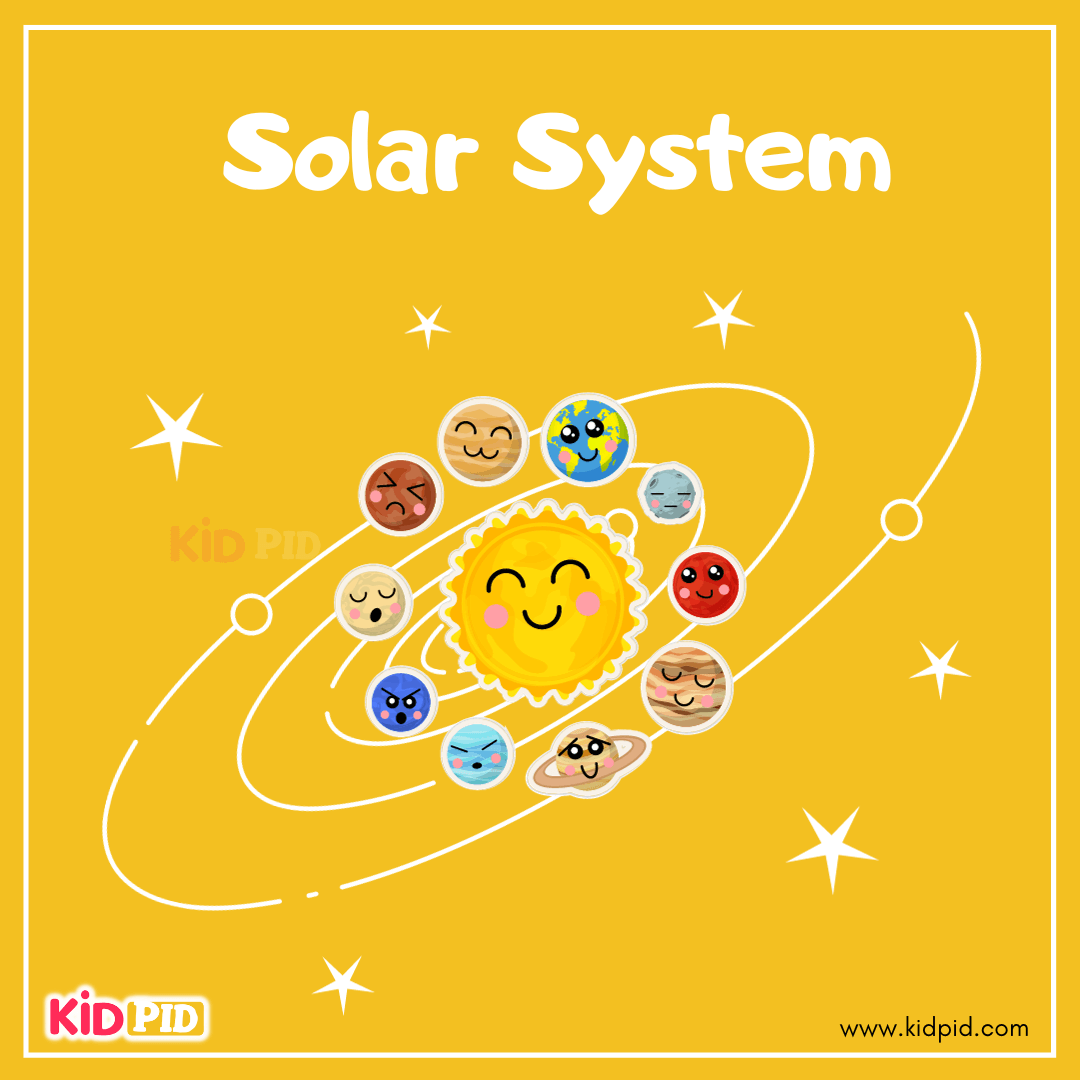
The solar system consists of the Sun and eight planets, including Earth. Each planet has unique characteristics, and exploring them helps kids understand space and science.
3D Planets Flashcards
3D planets flashcards are interactive learning tools showcasing realistic, three-dimensional representations of planets, helping users visualize and explore their physical features and orbits.
What causes the seasons on other planets?
Seasons on planets are caused by the tilt of their axis and their orbit around the Sun, which affects the amount of sunlight received.