Plants are essential for life on Earth. They provide us with food, oxygen, and help maintain a healthy environment. Different parts of a plant—like roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits—have special jobs. Each part works together to help plants grow strong, stay healthy, and provide us with many useful things.
[Scroll Down for Download Link]
Parts of Plants & Their Functions


Hi Kids! Today, we will learn more about plants and their differences.
Let’s get started!

Plants are one of the most important things in the world.

Without plants, there would be no food or oxygen for animals to breathe.

Plants have different parts, and each part has a different role.

Let’s learn more about the function of roots in detail

All plants have two main parts:
- Root
- Shoot

The part of the plant that remains under the soil is called the Root.

The part of the plant that remains above the ground is called a Shoot.

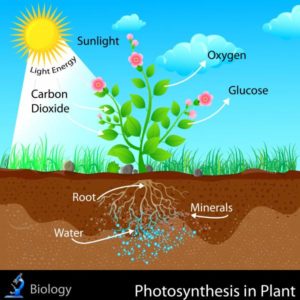
The main function of the shoot is to produce nutrients for the plant through photosynthesis and to complete the reproductive process.

The main function of roots is to anchor plants into the soil.

Roots take water and nutrients from the soil and store nutrients in some plants.

Roots absorb water from the soil and provide nutrients and minerals to plants.

As we need food and water, plants also need nutrients and minerals to grow strong and healthy.

Minerals and nutrients travel through the roots to the stems and other parts of the plant, providing nutrients to different parts of the plant.

Roots anchor the plant, which means roots fix the plant into the soil.

Roots hold the soil together, protecting it from rain or wind. So the roots are the support of the plant.

Some roots also store foods we eat, such as Carrots, Radish, and Turnips.

Now let’s look at the different types of Roots.

There are two main types of roots: Tap roots and Fibrous roots.

When a single thick tap root grows from the bottom of the stem, it is called a Tap root.

Beans, Carrots, Mangoes, Radishes, Roses, Hibiscus, and Turnips are plants that have tap roots.

Tap roots store nutrients, and we eat these roots.

The growth of many thin, dense roots from the base of the root is called a Fibrous system.

Grass, Corn, Bamboo, Coconut trees, Onions, Wheat, and Rice are plants with fibrous roots.

Let’s learn about the shoot of a plant.

The part of the plant that grows above the ground is called the Shoot.
Now let’s look at different parts of the shoot

Leaves, Petioles, Nodes, Buds, Flowers, Fruits, and Branches are all different parts of a branch, and each part plays a different role.

The stem is the main part of the plant that allows it to stand upright.

Leaves prepare food for plants through photosynthesis and are also called food factories for plants.

Flowers are the most beautiful of plants and the plant’s means of reproduction.

The fruit stores the food prepared by the plant and encloses the seeds inside.

Different types of plants have different types of stems.
Large trees have strong, hard, woody trunks.

Shrubs have brown, thick trunks but are not as thick as trees.

Herbs have green, soft stems.

Climbers and creepers have tender, green stems, making it impossible for the plant to stand upright.

Creepers and climbers need support from external objects to climb or crawl for longer periods.

Some stems are thick and juicy, such as Sugarcane.
Sugarcane is the thick, juicy fruit that humans eat.

Some stems remain underground and store nutrients like potatoes and onions, and these are the stems we eat.

In conclusion, the parts of a plant—roots, shoots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits—all play important roles in helping plants live and grow. Roots take water and nutrients, leaves make food, and flowers help plants reproduce. By learning about plants, we can better understand nature and how plants help all living things.
You may like this:
How do plants get water from the ground?

A clear, child-friendly article on how plants get water from the ground: explains that roots—with tiny hairs—absorb water via osmosis, then transport it upward through xylem to leaves.
Label Parts of a Plant Cell Worksheet

An educational Label Parts of Plant Cell Worksheet: kids learn to identify and label key plant cell structures—like nucleus, cell wall, chloroplasts—understanding each part’s role in helping plants survive and grow.
How does Water Reach the Top of the Tree from the Roots?

A clear, child‑friendly article on how water moves up trees from roots to leaves: explains osmosis in root hairs, xylem tubes, and leaf transpiration—working like a straw that pulls water sky‑high
Paragraph on ‘Flora and Fauna’

A simple, kid‑friendly paragraph on flora and fauna: explains plants and animals working together to keep nature balanced—plants provide air and food, animals spread seeds and pollinate flowers.
Plants can produce flowers, but we don’t. Why?
A simple, child‑friendly article titled “Plants Can Produce Flowers but We Don’t” explains that plants grow flowers and fruits through their unique structure and photosynthesis, while humans grow differently.







