A river is a channel of water, coursing through plain land and finally flowing in to the sea. Some rivers join with others and are called tributaries. But, the origin of a river is very interesting.
The origin of a river refers to its source, that is, the place from where the route of the river begins and as a general rule, this place is in the mountains or hills.
As we know, a river is a body of water, so its origin must also be a source of water. Normally a river begins, or starts, from a glacier, stream, or lake; a glacier may be explained as a body of ice. This starting point is called Headwater or Headstream.
Now, the question is, how is a river formed? In places of high altitude, like mountains or hills, we can see springs and a spring is formed when underground water naturally seeps out. Now when water from melted glacier and rain water is added to the spring, then a narrow channel of water is formed. This is called a rill and when other streams join this rill and more water is collected, the rill becomes a larger and bigger channel of water, known as gullies. Ultimately these gullies become big enough and a river is born.
Some examples of river origins are as follows:
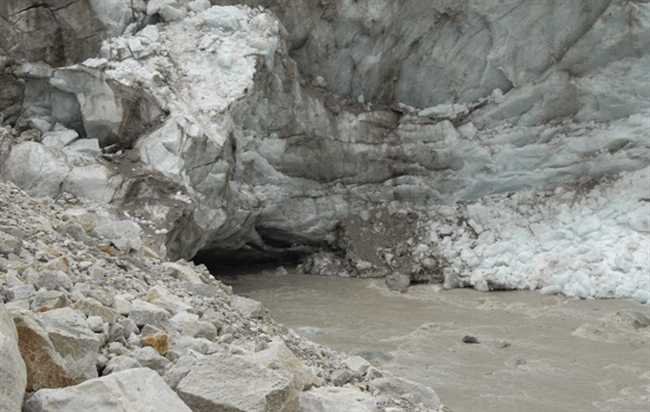
The origin of the river Ganga is the Gangotri glacier at Gomukh, a place in the Himalayas (picture below).
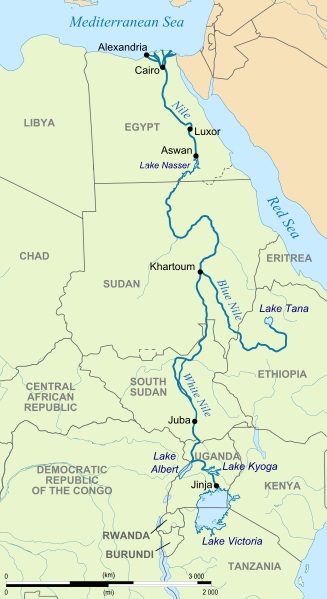
The picture below shows the course of the river Nile, originating from Lake Victoria.
You may like these:
Brief Paragraph on ‘The Importance of Oceans’

Oceans cover most of Earth, providing food, oxygen, and climate control. They support marine life, trade, and recreation, which is key in sustaining life globally.
Write a Paragraph on ‘Importance of Rivers and Lakes’

Rivers and lakes supply fresh water, support ecosystems, and aid agriculture. They help transport goods, prevent floods, and offer habitats for diverse species, benefiting both nature and humans.
Short Paragraph on ‘The Importance of Wetlands’

Wetlands filter water, reduce flooding, and house unique wildlife. They act as natural buffers, support biodiversity, and store carbon, making them vital for environmental balance.
Mini Paragraph on ‘Impact of Global Warming on Oceans’

Global warming heats oceans, causing rising sea levels and harming marine life. Coral reefs die, storms grow stronger, and ecosystems suffer, threatening coastal communities and economies.
How far down does the ocean go?

The ocean’s depth varies; its average is about 12,000 feet, with the deepest point, Challenger Deep, reaching nearly 36,000 feet below the surface.