Ancient India – Stone Age

- As you would have read earlier, people as early as two million years ago were hunters and gathers..
- Generally, they hunted wild animals and fish, gathered fruits, nuts, roots, stems, seeds and eggs.
- The hunters and gatherers usually moved from place to place. A few reasons are as follows:
-
- After staying at a place and eating up all the animals and plants there, they would go elsewhere in search of food.
- Animals move from place to place in search of food and shelter. That is why those who hunted them had to follow their movements.
- In search of seasonal fruits. Seasonal fruits did not grow everywhere. They had to move from place to place, changing locations according to the season.
- People, animals and plants need water to survive. Water is found in lakes, streams and rivers. While many rivers are perennial (have water throughout the year), others are seasonal and only have water mainly during the rainy season. People living on the banks of perennial rivers had to move in search of another source of water when they dried up in summers and winters.
- Meeting their family and friends.
Contents
How do we know about them?
We know about these people through archaeological evidence such as:
- Tools of stone, wood and bone, to cut meat, chop fruits and roots.
- Some stones had handles attached to make arrows and spears for hunting.
- Some were used as an axe to chop wood for firewood and building huts.

Choosing Place to Live
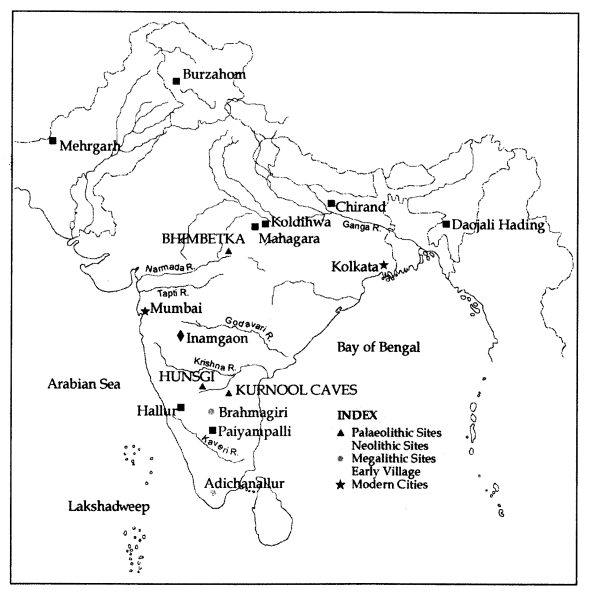
- Many sites were located near source of water such as lakes and rivers.
- People also preferred places where stones were available.
Fun fact: Places where stones were found and their tools were made are known as factory sites. We come to know about these sites by finding remains of discarded tools and stones there.
Factory sites where people lived around for a longer spell of time are called habitation-cum-factory sites.
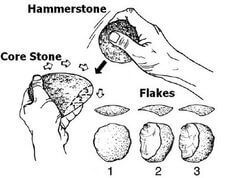
Making Stone Tools
Stone making techniques:
- Stone on stone: The pebble from which tool was to be made was held in one hand and another stone, held in the other hand was used as a hammer to give shape.
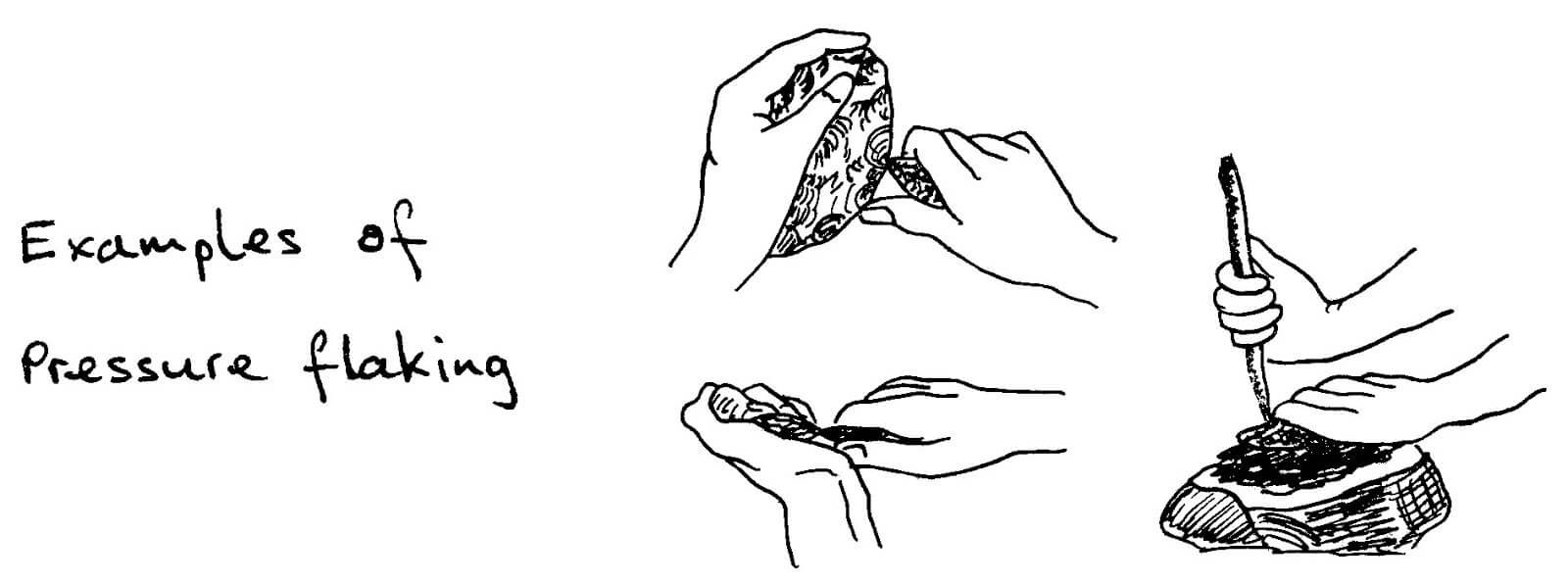
2. Pressure flaking: The stone (say stone 1) was placed on a firm surface. The hammer stone was then used on a piece of bone or stone that on on top of the stone 1 to remove its flakes to give it a shape.
Discovery of Fire
- Find Kurnool cave in the map. Traces of ash from fire has been found here.
- Fire could have been used to – 1. drive away animals, 2. as a source of light, 3. to cook meat, 4. for warmth.
Major Changes 12,000 Years Ago
- Development of grasslands: This led to the increase in animals like deer, sheep, goat, cattle who survived on grass.
- Impact on hunters: The hunters now followed these animals, paying attention to their food habits and breeding seasons. This was the time when people started thinking of herding and rearing these animals themselves.
- People got familiar with grain bearing plants such as wheat, barley, etc, that grew automatically in favourable places.
Rock Paintings
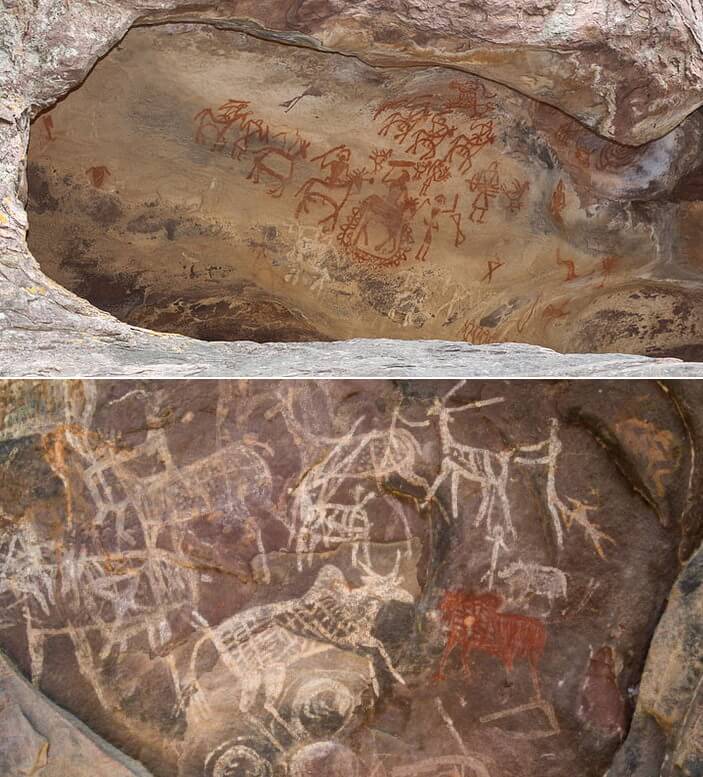

- Many of the caves in places like Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, etc have wall paintings in them.
- These paintings show wild animals, drawn with great accuracy and skills.
Terms to know
Palaeolithic age– palaeo: old + lithos: stone
- This is a name given to the period about which we studied just now.
- This period has great use of stone in it.
Mesolithic age: middle stone
- This period in history saw great environmental changes.
- Stone tools found belonging to this age are generally tiny and are called microliths.
You will learn about Neolithic age soon.






Responses