Reproduction is an essential process to ensure the continuation of life on earth and it is very important in maintaining balance of the ecosystem.
Reproduction in animals gives rise to their offspring. For example, dogs reproduce to give birth to young puppies, cows give birth to calves and so on.
Contents
Activity:
Find out what the offspring of the following animals are called –
- Chicken
- Horse
- Cat
- Frogs
- Tiger
Types of Reproduction:
Reproduction in animals is of two main types – Sexual Reproduction and Asexual Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction:
Sexual reproduction is characterized by fusion of a male gamete with a female gamete resulting in the production of a zygote. The new offsprings develop from this zygote.
Male gametes are generated by the male reproductive organs and female gametes are generated by the female reproductive organs.
First let us understand the male and female reproductive organs of humans and the gametes produced by them.
Female Reproductive System of Human:
- A pair of ovaries along with a pair of oviducts (fallopian tubes) and the uterus constitute the female reproductive system.
- The female gamete is known as the egg or ovum (plural – ova). It is a single cell. It is produced by the ovaries.
- In human beings, a single mature egg or ovum is released by one of the ovaries, once a month, into the fallopian tube.
- The uterus is a hollow, pear-shaped organ where the baby develops.
Male Reproductive System of Human:
- The male reproductive system consists of a pair of testes (singular – testis), two sperm ducts and a penis.
- The male gamete is known as sperm.
- Millions of sperms are produced by the testes.
Structure of sperm
Sperm consists of a head, a neck and a tail. The tail helps the sperm to move towards the egg.
Fertilisation:
When a sperm comes in contact with an egg, it penetrates the egg. The nucleus of the sperm fuses with the nucleus of the egg to produce a single nucleus – this is the fertilized egg or zygote. This process is known as fertilization and the zygote is the product of fertilization.
Thus we can see that a male gamete or sperm derived from the male parent fuses with the female gamete or egg derived from the female parent to give rise to the zygote which eventually develops into the offspring. This is why offspring have characteristics similar to their mother and their father.
Types of Fertilization:
Internal Fertilization
Fertilization that takes place inside the female body is known as internal fertilisation. Humans exhibit internal fertilization as well as dogs, cats, cows, horses, etc.
External Fertilization
Fertilization or fusion of male and female gametes that takes place outside the body is known as external fertilization.
Let’s try to understand external fertilization by studying the process of fertilization in frogs.
- In monsoon, frogs move to ponds and slow-flowing streams
- The female frog lays hundreds of eggs in the water; these eggs are not covered by a hard shell like a chicken’s egg, they are very delicate and are held together by layer of jelly which also provides protection
- The male frog deposits sperms over the eggs
- The sperms swim to the eggs using their tail and initiate zygote formation.
- This entire process of fertilization which takes place outside the body is known as external fertilization.
Animals such as fish, starfish, etc. show external fertilization.
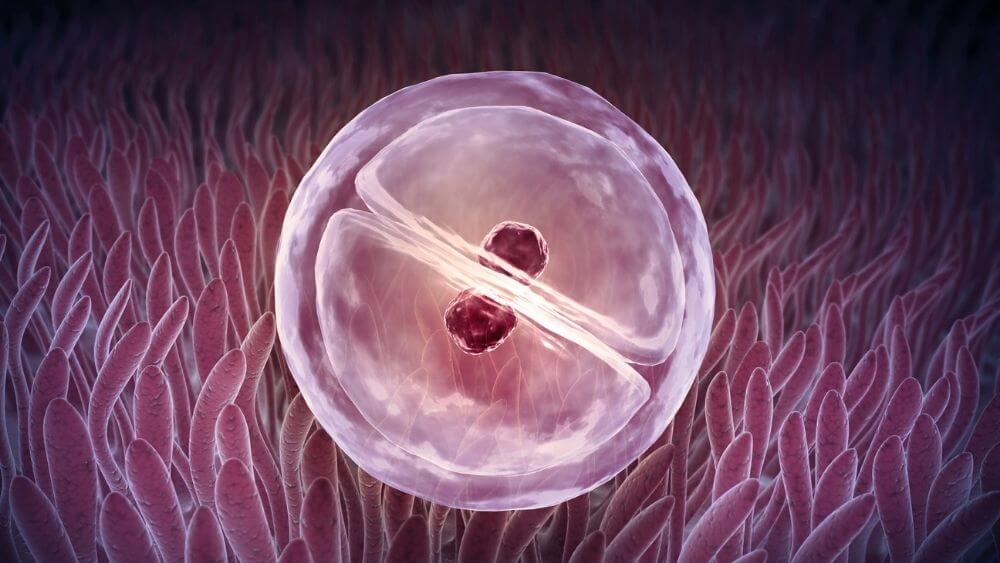
Development of Embryo:
- The zygote differentiates or divides repeatedly to give rise to a mass of cells.
- The mass of cells are then divided into separate groups and each of these groups then form tissues and different organs of the body.
- This developing structure is known as the embryo.
- The embryo is embedded in the uterus where it gradually grows and develops.
- When the different body parts of the embryo can be distinguished such as hand, legs, feet, eyes, nose, etc, it is known as the foetus.
Now, we all know that hens lay eggs and new-born chicks hatch from these eggs but hens actually exhibit internal fertilization. This is because the fusion of the male and female gamete i.e., fertilization occurs inside the female chicken. As the zygote descends along the fallopian several protective layers develop around it and the hard shell is eventually formed around the developing embryo. The hen then lays the egg and eventually the egg hatches to give a chick.
On the other hand, in external fertilization, development of the embryo takes place outside the body.
Viviparous and Oviparous Animals:
Animals that give birth to their young are known as viviparous animals.Humans, cats, dogs, cows, etc are all viviparous animals.
Animals that lay eggs are known as oviparous animals. Animals such as ducks, pigeons, crows, fishes, etc are all examples of oviparous animals.
Development of Offsprings into Adults:
New-born animals continue to grow and develop into adults. However in some animals, the adult form is completely indistinguishable from the new born. Let’s take the example of frogs. The life cycle of a frog is as follows:
Egg→ Tadpole(larva) → Adult Frog
A similar life cycle is observed in moths.
Egg→ Larva or caterpillar → Pupa → Adult Moth
We can see that in both of these cases the adults possess several developed characteristics that are not found in the newborn.
The phenomenon in which a larva transforms into an adult through drastic changes is known as metamorphosis.
Asexual Reproduction:
The process by which a single parent gives rise to offspring is known as asexual reproduction.
Microscopic animals such as amoeba, hydra reproduce asexually. Let us look at how these animals reproduce asexually.
Amoeba:
Amoeba is a unicellular, microscopic animal. It can only reproduce through asexual means. The process is as follows:
- The nucleus within the cell first divides to give rise to two nuclei.
- The cell then divides and each part receives a single nucleus.
- Finally, two cells are produced from a single-celled parent.
- This entire process is known as fission.
Hydra:
Hydra are microscopic organisms. They reproduce asexually as follows:
- Small outgrowths or buds develop on various parts of the body of hydra.
- These buds detach from the parent.
- The detached buds grow and eventually develop into adult hydra; multiple offspring arise from a single parent
- This process of asexual reproduction is known as budding.
Summary:
- Types of reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction
- Human male and female reproductive system
- Fertilization
- Internal and external fertilization
- Development of embryo
- Viviparous and oviparous animals
- Metamorphosis
- Asexual reproduction
- Fission
- Budding