Reproduction in Plants
Reproduction is the formation of offspring from parents. It is a basic character of a living being, both plants and animals.
Contents
Reproduction can be various types:
- Asexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction
- vegetative propagation
1. Asexual Reproduction:
Type of reproduction in which seeds are not formed.
- Budding- a bud grows in the main parent plant and gets detached to form new plant. For example: Yeast
- Fragmentation- A parent’s body breaks into small fragments and new individuals are formed from the fragments. For example- ferns and Fungi.
2. Vegetative Propagation:-
When formation of new plant begins from the vegetative parts of a plant (leaves, root, stems), such type of reproduction is known as Vegetative Propagation.
Examples:
- Potato- new plants begin to develop from the eyes of a potato.
- Ginger- a new plant begins to develop from the margins of a ginger.
- Bryophyllum- new plant begins to develop from the margins of leaves of the parent plant.
3. Sexual Reproduction:-

In sexual reproduction,
- two parents and gametes are involved
- fertilization takes place
- zygote is formed
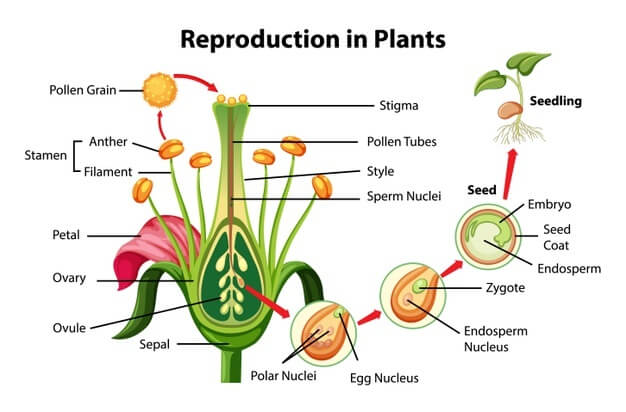
Flower:
A flower has different parts or whorls, namely-
- calyx- sepals
- corolla- the petals
- androecium- the male reproductive organ composed of anthers (containing pollen) and a filament
- gynoecium- the female reproductive organ composed of stigma, style and ovary( with ovules contained in the ovaries)
Flowers can be:
- Unisexual- male and female whorls are present in different flowers.
- Bisexual- both male and female whorls are present in same flowers.
Pollination:
The transfer of pollens from the stamens to the stigma of the same/different flowers is known as pollination.
Types of pollination:
- Self Pollination- The transfer of pollens from the stamens to the stigma of the same flowers is known as self pollination.
- Cross Pollination-The transfer of pollens from the stamens to the stigma of the different flowers is known as cross pollination.
Fertilization
The fusion of the male (pollen) and the female (ovules) gametes that leads to the formation of a zygote is known as fertilization.
Mechanism:
- pollens from the stamens are transferred to the stigma
- through the stigma, a pollen tube is formed that emerges from the pollen pore
- through this tube, the male nuclei present in the pollen reaches the ovule
- the male nuclei fuses with the egg cell in the ovule that leads to the formation of the zygote
Fruits and seeds
The fruit is the ripened ovary and the seeds of a fruit are the ovules of the ovary.
Dispersal of seeds:
When an organism eats a fruit, its seeds might get dispersed through wind/might get attached to anything and then get dispersed. When these seeds meet the favorable environmental conditions, they might grow into new plants.
This was the summary of what happens when a plant reproduces, how a fruit is formed and why are flowers necessary. Let’s protect our trees and plant more saplings. They’ll grow into beautiful plants with flowers that will not only soothe your eyes but will also provide fruits.





Responses