States of Water
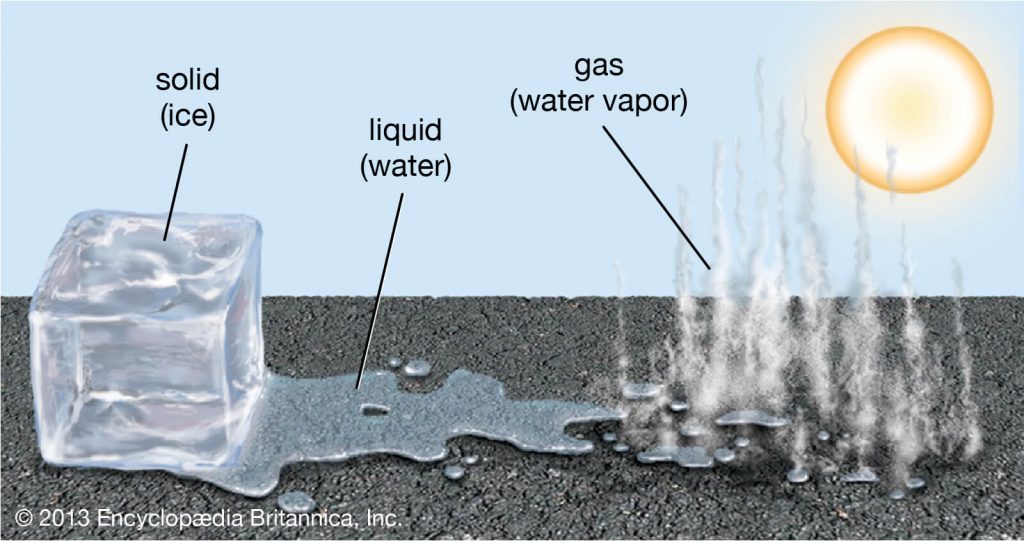
This topic can be referred to as an extended part of the topic ‘States of Matter’. We know that normally, matter exists in 3 states, that are solid, liquid, and gas.
In this topic, we are going to discuss the three states of water as water exists or can exist in all three states.
Contents
1. Solid State
Water can exist in a solid-state. Do an experiment at your home. Take a glass of water and keep it inside the deep freezer. After some hours, take it out. What do you see?
The result of this experiment is that water which was in a liquid state turned into Ice, which is solid. Snow, frosts, and Ice are an example of Water in solid-state.
2. Liquid State
We all know the example of water in a liquid state. The liquid drinking water which we always drink, that is the most common example.
Due to the way of the orientation of Hydrogen Bonds during it’s freezing, water has a lower density in its solid form, which is an exception. In comparison to the water in a liquid state, water molecules are pushed more apart.
As for any other liquid, they turn into solid only when the temperature drops, packing the solid tighter than the previous state, which results the solid to have greater density.
3. Gaseous State
Water turns into its gaseous state after evaporation. Examples are steam and water vapor.
When heated, the hydrogen bonds of water completely breaks as the kinetic energy rises, causing the molecules to turn into the gaseous state, that is, into steam or vapor.





Responses