World War II
World War II or the Second World War involved virtually every part of the world during 1939-45. Opposite to each other in the war were the Axis powers – Germany, Italy, and Japan and the Allied powers/Allies — France, Great Britain, the United States and the Soviet Union (USSR).
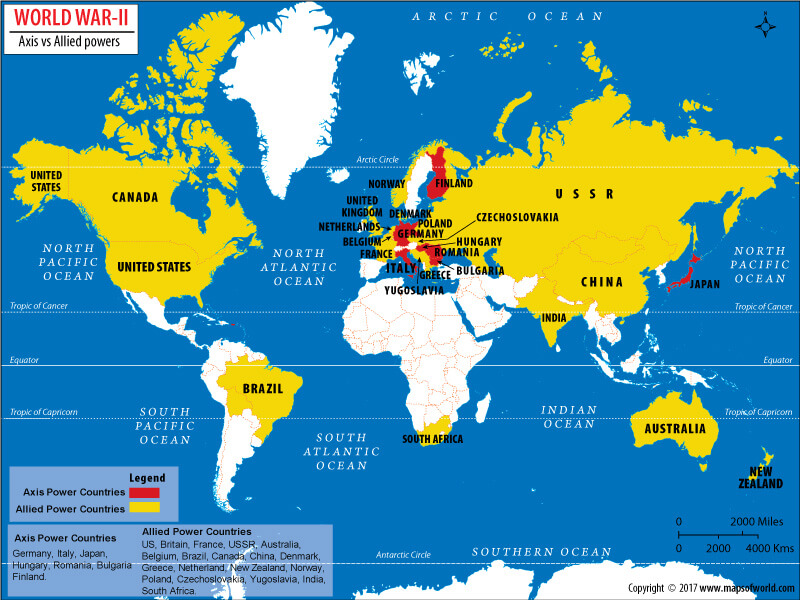
The instability created in Europe by the WWI (1914-18) led to this conflict which broke out just two decades later and came out to be much more devastating than its predecessor. The rise of Adolf Hitler, the leader of the Nazi Party, in an economically and politically unstable Germany, rearmed the nation. He signed treaties on behalf of Germany with Italy and Japan to live his ambitions of world domination.
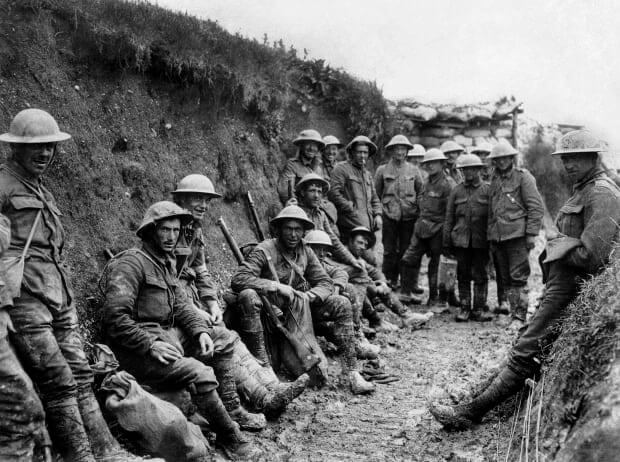
Germany, under the leadership of Hitler, invaded Poland in September 1939. To this, Great Britain and France reacted by declaring war on Germany, marking the beginning of World War II or WWII. The six years long conflict that followed took more lives and destroyed more land and property around the world more than any previous war. Approximately 50-80 million (4-6 crore) people were killed, from which 6 million (60 Lakh) were Jews, who were killed in Nazi concentration camps.
The war resulted in the extension of the power of the Soviet Union in Eastern Europe, enabled a communist movement in China, and marked a prominent shift in the world power away from western Europe to the United States and the Soviet Union, that resulted into a long Cold War between them.
Contents
Hitler and his Idea of ‘Lebensraum’
The devastation of WWI in Europe left the continent destabilised. Meanwhile, frustration and resentment from seclusion of Germany from world affairs, such as the League of Nations and the Treaty of Versailles as a punishment, kept growing in the country violently. This fuelled the rise to power of Adolf Hitler and the National Socialist German Workers’ Party (NSDAP) or the Nazi Party in Germany.
After Hitler rose to power and became the Chancellor of Germany in 1933, he declared himself the supreme leader. He was obsessed with the idea of the superiority of the ‘pure’ German race, or the “Aryan”, and believed of war being the only way to gain ‘lebensraum’ or living space for the original German race to expand.

Leading up the Second World War
After signing alliances with Italy and Japan against the Soviet Union, Hitler sent his troops to occupy Austria in 1938. The following year, he annexed Czechoslovakia too.
While the United States and Soviet Union were concentrated on their internal affairs at the time, and France and Britain were less than eager for confrontation, Hitler’s open aggression went unchecked.
The Outbreak
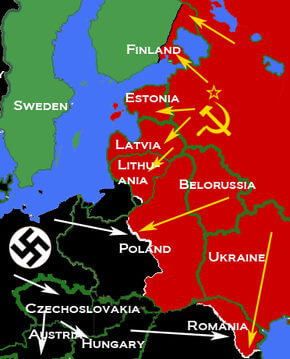
In August 1939, Hitler and Soviet leader Joseph Stalin signed the German-Soviet Nonaggression Pact, which said that Hitler would not face a war on two fronts after he invaded Poland, and would have Soviet assistance in winning over and dividing the nation. On September 1, 1939, Hitler invaded Poland from the west. Two days later, France and Britain declared a war on Germany in response. Hitler had long planned to invade Poland, a nation to which Great Britain and France had guaranteed military support if attacked by Germany.
On September 17, 1939, Soviet troops invaded Poland from the east. Under attack from both sides, Poland lost. By early 1940, both the invading forces had divided control over the nation, based on a protocol in the non-aggression pact. Soviet forces under Stalin then moved to occupy the Baltic states (Latvia, Lithuania and Estonia) and defeated Finland.
War in the West (1940-41)
Invasion of Norway and Denmark
In early April 1940, Germany invaded Norway and occupied Denmark, and the war began henceforth. Denmark surrendered on the same day whereas, Norway held out until early June before German forces could occupy the entire country.
Invasion of Western Europe
That same year on May 1940, Germany invaded France and the neutral Low Countries- the Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg. The Low Countries were defeated by Germany by the end of May. France signed an agreement with Germany providing for the German occupation of the northern half of France.
Hitler now turned his attention to Britain. German planes bombed Britain extensively from September of 1940 to the May of 1941. The Royal Air Force eventually defeated the German Air Force in the Battle of Britain. With Britain’s defensive resources moving closer to the post of exhaustion, they started receiving crucial aid from the U.S.
Operation Barbarossa
By early 1941, Germany successfully encouraged Hungary, Romania, Slovakia and Bulgaria to join the Axis. German troops overran Yugoslavia and Greece in April 1941. Hitler’s conquest of the Balkan land was backed by his real objective to invade the Soviet Union, whose vast territory would give the German ‘master race’ the living space it needed. The other reason was to kill the Jews from throughout German-occupied Europe.
On June 22, 1941, Hitler invaded the Soviet Union in the attack called Operation Barbarossa. Despite outnumbering the German aircrafts and tanks, Russian defence stood weak against the German army due to their largely obsolete aviation technology.
By the end of October 1941, German troops had advanced deep into the Soviet land. The Red Army of Soviet Union resisted the Germans from capturing the key cities of Leningrad and Moscow. On December 6, 1941, a counteroffensive was launched by the Soviet troops that drove the Germans permanently from the outskirts of Moscow.
The United States Enters the War
On December 7, 1941, Japan launched a surprise attack on Pearl Harbour, Hawaii. 360 Japanese aircraft attacked the major U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbour, claiming the lives of more than 2,300 troops. In response, the United States declared war against Japan and Great Britain followed the US. On December 11, Germany and Italy declared war on the United States.
After a long chain of Japanese victories, the U.S. Pacific Fleet won the Battle of Midway in June 1942, which stood as a turning point in the war. In August 1942, US forces halted the Japanese from making any further advancements in the Pacific islands.
Toward Allied Victory in World War II (1943-45)
The British and American forces had defeated the Italians and Germans in North Africa by 1943. On the Eastern Front, a Soviet counteroffensive in November 1942 ended the Battle of Stalingrad (military campaign between Russian forces and those of Nazi Germany during WWII; the battle is infamous as one of the largest, longest and bloodiest engagements in modern warfare) with the German troops surrendering on January 31, 1943.
D-Day
The Allies began a massive invasion of Europe on June 6, 1944, landing 1,56,000 British, Canadian and America soldiers on the beaches of Normandy, France. This day is remembered as ‘D-Day‘ because it was the largest military naval, air and land operation ever attempted and marked the start of the campaign to liberate Nazi-occupied north-west Europe. In response, Hitler deployed all of his armies into Western Europe, resulting in German defeat in the East. By December, all of France, most of Belgium, and part of southern Netherland had been freed. Hitler poured all the remaining strength in the Battle of the Bulge, which turned out to be the last German offensive in the war. It lasted for six brutal weeks, from December 16, 1944, to January 25, 1945. Hitler’s aim was to split the Allies in their drive toward Germany.
The Allied invaded Germany after an intensive aerial bombardment in February 1945. Germany formally surrendered on May 8. Hitler was already dead, having died by suicide on April 30 in his bunker.
Defeat of Japan
British and US forces began slowly to move northward toward the Japanese mainland, after clearing the Japanese from the Solomon Islands in November 1942. The British forces simultaneously worked with the Nationalist Chinese government to fight the Japanese in China.
US troops landed in the Philippines in the October of 1944. By May of 1945, the British and US troops had conquered the last major Japanese base before the mainland itself.
Developed during a top-secret operation code-named The Manhattan Project, the atomic bomb was unleashed on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. On August 6, 1945, the United States dropped the first atomic bomb on Hiroshima, following with a second atomic bomb on Nagasaki on August 9. On August 8, the Soviet Union declared war on Japan and invaded Japanese-occupied Manchuria.


Less than a week later, on August 14, 1945, Japan agreed to surrender; the formal ceremony took place on September 2. World War II was over.
World War II Casualties
This deadliest international conflict in history resulted in approximately 55 to 80 million deaths worldwide (the variations in the following statistics are subject to different available source material), including 6 million Jews who died at the hands of the Nazis during the Holocaust.
Millions were injured, and still more lost their homes and property.
References:
https://encyclopedia.ushmm.org/content/en/article/world-war-ii-in-depth
https://www.history.com/topics/world-war-ii/world-war-ii-history
Quiz Time!
- What event led the United States to join the war?
- Explain what happened on ‘D-Day’?
- Explain Hitler’s ideology of ‘Lebensraum’.
- Write a short note on World War II in your own words.
- Fill in the blanks:
a. Hitler was obsessed with the idea of the superiority of the ‘pure’ German race, or the _______, and believed of war being the only way to gain ___________ or living space for the original German race to expand.
b. In August 1939, Hitler and Soviet leader Joseph Stalin signed the __________________ which said that Hitler would have Soviet assistance in winning over and dividing Poland.
c. Latvia, Lithuania and Estonia are together called the ______________.
d. On June 22, 1941, Hitler invaded the Soviet Union in the attack called ____________.
e. Despite outnumbering the German aircrafts and tanks, the Russian defence could win over the Germans because _________________________.
f. On _____________, Japan launched a surprise attack on a major U.S. naval base called _____________ in Hawaii.
g. Theatomic bomb developed during The Manhattan Project, was unleashed on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima on __________ and ________ on ___________.






Responses