Ancient Mesopotamia

- Mesopotamia is a combination of the Greek word meso (in between) and potamia (potamus- meaning river)
- The civilisation was on the banks of the river Tigris and Euphrates and included parts of modern day Iraq (largest part) , Kuwait, Turkey and Syria
- Early civilisations began to form around 12000 BCE (Before Common Era).
- Some majorly known Mesopotamian civilisations include the Sumerian, Akkadian, Babylonian and Assyrian.
- Archaeological evidence shows extensive use of technology, literature, religion and agriculture in the societies.
- Women enjoyed equal opportunities as men. Both of them took part in agriculture (principle occupation in empire) and trade.
Contents
Importance of rivers in early civilisations
- Roughly 6000 to 8000 years ago, most of the well known civilisations, such as in Ancient Egypt along river Nile; the Indus Valley civilisation, were formed along river banks. This makes us wonder the significance of these water bodies to the civilisation.
- The ancient people fed themselves with the food from either hunting or agriculture. Sometimes, when it rained too much, the rivers caused floods. The farmers in Sumer (the earliest civilisation in Mesopotamia) created levees to hold back the floods from their fields and cut canals to channel river water to the fields. The use of levees and canals is called irrigation, another Sumerian (belonging to Sumer) invention.
- Floods could destroy crops but they also brought silt or fertile soil along with them. The fertile soil brought was used by the people to perform agriculture. They also provided water for irrigating the vegetation as well as drinking. Availability of fertile soil attracted people to shift to the banks of this river as thus, this is no coincidence that some of the world’s first civilisations developed in such areas as well.
Ancient Mesopotamia: The cradle of civilisation
- Mesopotamia, also referred to as the ‘cradle of civilisation’, because of being the birth spot of the most famous early empires, was one of the first places where agriculture was developed.
- It was also in contact with the Egyptian and the Indus Valley civilisations which made it a hub where different languages and cultures met.
- The writings, technology, language, trade and religion in Mesopotamia was born thus.
- The civilisation was a collection of various cultures bound by a common script and their gods (whose names sometimes differed from region to region).


Fun fact– Did you know, the credit for invention of wheel is also given to the Mesopotamians. The remains of four-wheeled wagons, which was excavated in 1922 CE in the ancient site ‘Ur’, are said to be the oldest wheeled vehicles in the history ever found. Other important inventions include- domestication of animals, agriculture, common tools, classification of time into hours, minutes and seconds, sailboats, and the list goes on [there have been 39 ‘firsts’ listed that originated from the civilisation].
Trade
- As we have talked earlier, the fertile conditions allowed the hunter-gatherer population to settle in the land, domesticate animals or perform agriculture.
- Trade soon emerged. The Mesopotamians traded pottery, grains, cooking oil, leather goods, textiles, baskets, jewellery, etc in return of Egyptian gold, Indian ivory and pearls, Arabian copper and Persian tin. The city-states traded with each other too.
- Traders soon started settling in urbanised areas of the civilisation. This gave birth to cities.
- It is generally thought that writing in Mesopotamia was invented due to trade to far away lands, to have communication, and to record the trade.
Jobs
- Ancient Mesopotamia was basically an agriculture based society and the principal occupation was growing crops and domesticating animals.
- There were also several other popular occupations like priest, artisan, weaver, shoemaker, potter, etc.
- Women had equal rights. They could own land, run businesses and make contracts in trade.
Sumer Civilisation
- The Sumerians (people of Sumer) were the first people to migrate to Mesopotamia.
- Around 5,500 years ago, they built cities along the Lower Mesopotamia.
- The cities had deserts around them.
- When cities grew, they acquired the area around them, thus creating city-states.
- Characteristics of cities:
- Each city state had their own government.
- Some historians believe that every city-state was surrounded by a large wall and had its own government.
- Sometimes, the city states fought each other for control over river water. Thus creating need for individual armies.
The Sumerians were divided into various social classes. Here is the hierarchy chart:
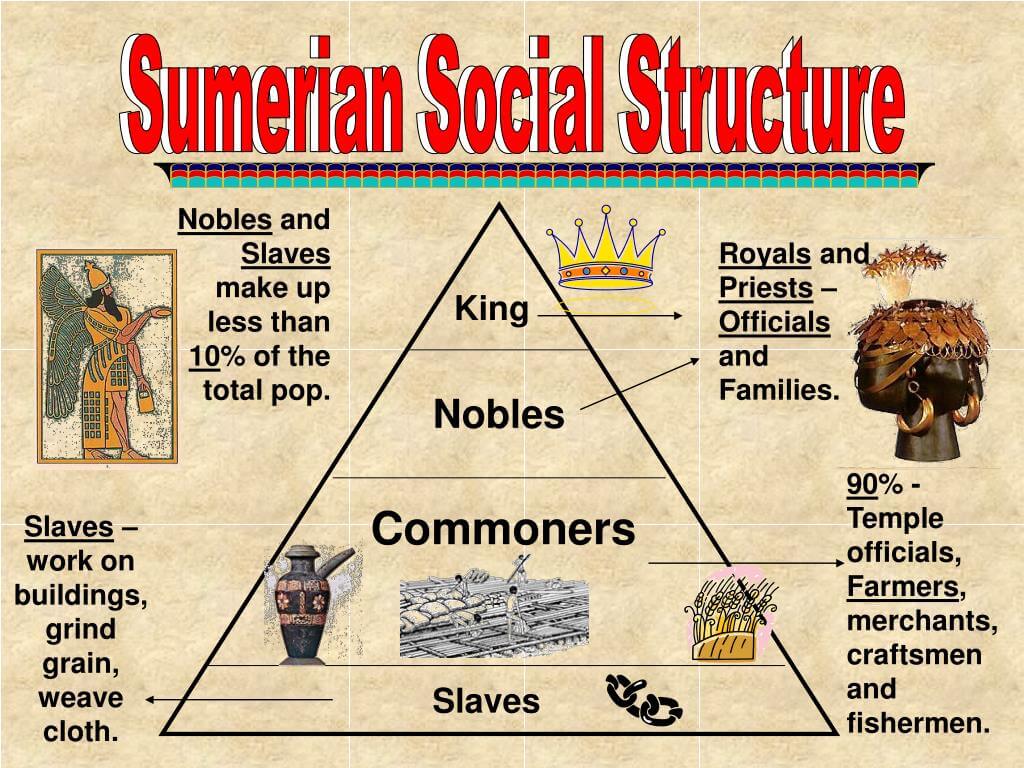
Gods & Religion
- The Sumerians worshipped many Gods.
- Each city-state claimed one god to be their own. Temples built for these gods were called ziggurat, a large pyramid shaped building with a temple on its top.

Later empires- Akkad, Babylon and Assyria
Around 2,300 BCE, the city-states of Sumer were conquered by the Akkads.
- The Akkads was the second ancient empire of Mesopotamia.
- Akkad was located in the northern division of ancient Babylonia.
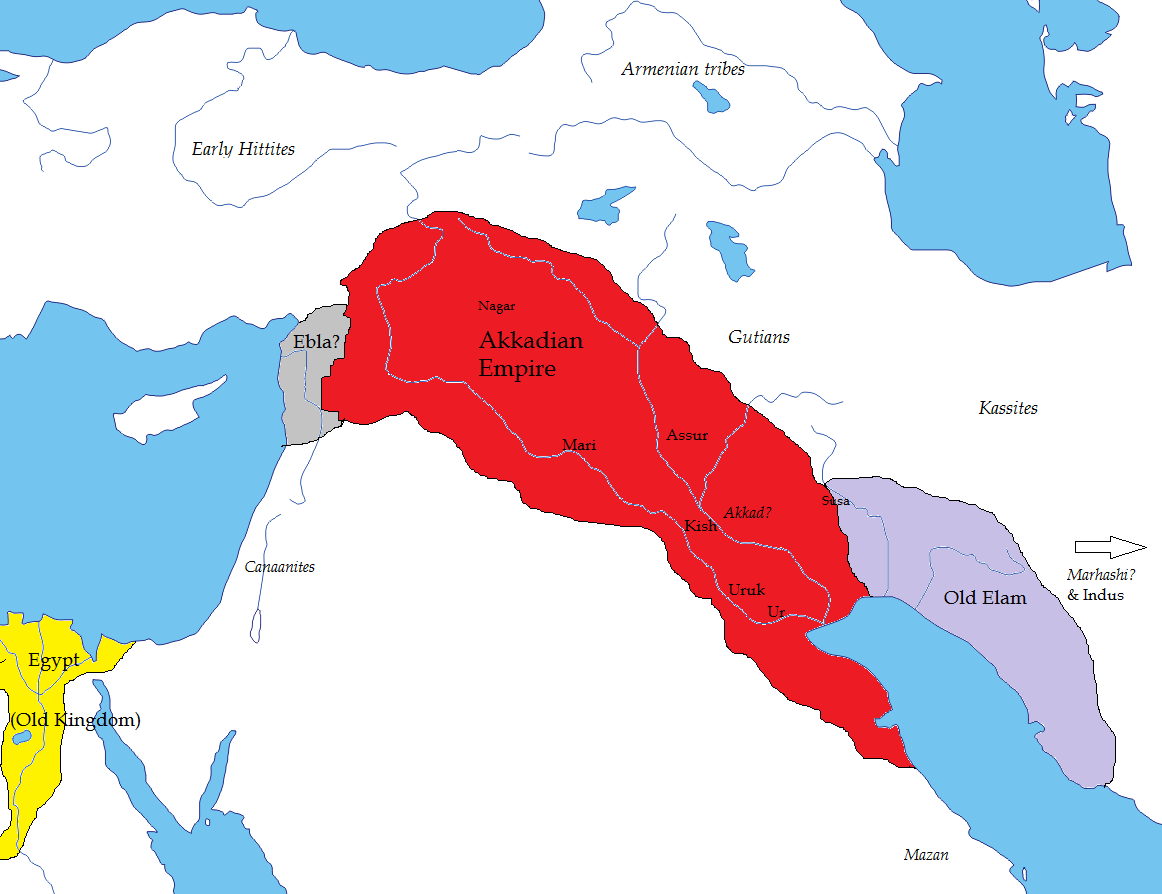
Fun fact: The language spoken by most of the people throughout the history of Ancient Mesopotamia is Akkadian.
- After the fall of Akkad empire, King Hammurabi founded the Babylonian Empire, which was named after his capital city. His rule is known for its peace, friendly relations with other cities and the Code of Hammurabi (set of laws in his empire carved on 8 feet stones). The empire also advanced in Mathematics, astronomy and trade.
- The empire was founded over 4000 years ago as a small port town on the Euphrates river.
- It grew into one of the largest cities of the ancient world under the rule of King Hammurabi who ruled from 1792 to 1750 BCE merging southern and central Mesopotamia under a unified Babylonian rule.
- The Babylonian people were the first to write down and record their system of law.
- As we can see, Babylon was short-lived. The empire fell apart after Hammurabi’s death into several small kingdoms.
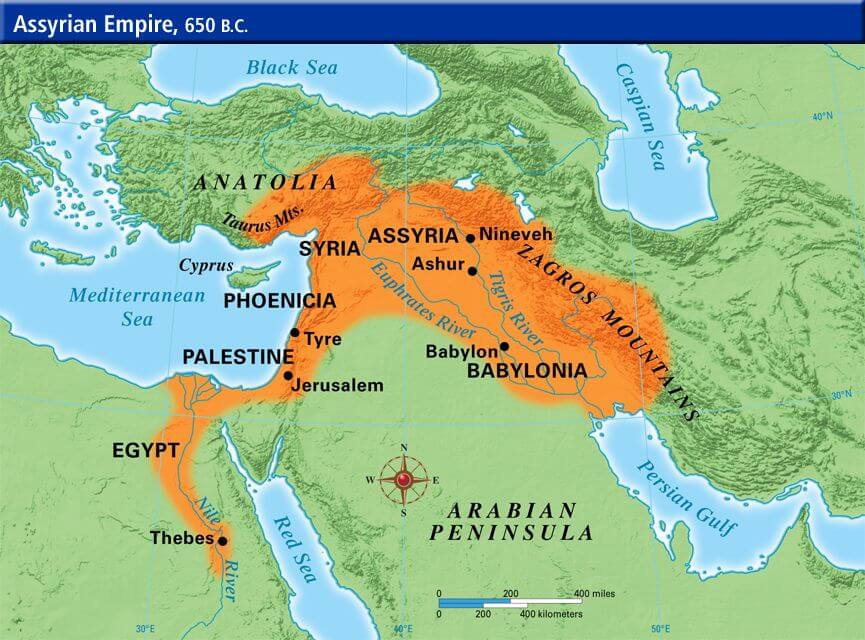
The Assyrians lived in northern Mesopotamia near the start of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers.
- They first rose to power when the Akkadian empire fell.
- The Babylonians had control of the south of Mesopotamia and the Assyrians had the north.
- One of the strongest leaders during this time was King Shamshi-Adad under whom, the empire expanded control over much of the north.
- However, after his death in 1781 BCE, the empire grew weak and Babylonians took control over them.
- The second wave of growth came in 1360 BCE. This time they conquered all of the Mesopotamia and expanded the empire to include the Middle East including Egypt and Babylonia.
- They were also known as the warrior society.
Practise Questions
Q. How was the geography of Mesopotamia helpful in its civilisation?
Q. What does Mesopotamia literally mean? What else is it called?
Q. What was the first human civilisation formed?
Q. What is the script developed by the Mesopotamians known as?
[Ans. Cuneiform]
Q. Describe the jobs done by Mesopotamians.
Q. Describe the social structure in Sumer.
Q. What is the Code of Hammurabi?






Responses